Cataloguing Strategic Innovations and Publications
Unleashing the Power of Business Analytics: A Guide to Success

In today's data-driven world, businesses are increasingly recognizing the importance of leveraging data to gain a competitive advantage. This is where business analytics comes into play. Business analytics encompasses a wide range of techniques and practices that enable organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights. In this article, we will explore the importance, applicability, uses implementation approach, and best practices of business analytics.
Business analytics refers to the practice of using data analysis and statistical methods to extract meaningful insights and make informed decisions in a business or organizational context. It involves collecting, organizing, and analyzing large volumes of data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships that can help drive strategic planning, operational efficiency, and overall business performance.
Business analytics combines various techniques from statistics, data mining, predictive modeling, machine learning, and data visualization to transform raw data into actionable information. It involves several key steps:
1. Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from multiple sources, such as transaction records, customer interactions, website analytics, social media data, and more. This data can be both structured (e.g., databases) and unstructured (e.g., text documents).
2. Data Cleaning and Preparation: Ensuring the data is accurate, complete, and formatted properly. This involves removing duplicates, handling missing values, standardizing data formats, and transforming data into a suitable format for analysis.
3. Data Exploration: Exploring the data to understand its characteristics, uncover patterns, and identify potential relationships. This can involve descriptive statistics, data visualization, and exploratory data analysis techniques.
4. Statistical Analysis: Applying statistical techniques to analyze the data and uncover insights. This may involve hypothesis testing, regression analysis, time series analysis, clustering, classification, or other statistical methods depending on the specific business problem.
5. Predictive Modeling: Building models to forecast future outcomes or predict specific events. This can involve techniques like regression analysis, decision trees, random forests, neural networks, or other machine learning algorithms.
6. Data Visualization and Reporting: Presenting the results of the analysis in a clear and visually appealing manner using charts, graphs, and dashboards. This enables stakeholders to easily understand the insights and make informed decisions.
7. Decision-Making and Implementation: Using the insights gained from the analysis to support decision-making processes. This can involve optimizing business operations, identifying market trends, improving customer experiences, optimizing pricing strategies, or any other area where data-driven insights can be applied.
Business analytics can provide numerous benefits to organizations, including:
· Improved decision-making: By providing accurate and timely insights, organizations can make informed decisions that are backed by data rather than relying solely on intuition or gut feelings.
· Enhanced operational efficiency: Analyzing data can help identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and improve resource allocation, leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
· Better customer understanding: Analyzing customer data can help businesses understand customer preferences, behavior, and needs, enabling them to personalize marketing efforts, improve customer satisfaction, and increase customer retention.
· Competitive advantage: By leveraging data analytics, organizations can gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends, predicting customer behavior, and making proactive strategic decisions.
Overall, business analytics enables organizations to harness the power of data to gain valuable insights, optimize operations, and make informed decisions that drive business success.
Importance of Business Analytics:
Business analytics has become crucial for organizations across industries due to the following reasons:
1. Informed Decision Making: By analyzing data, organizations can make data-driven decisions rather than relying on intuition or guesswork. Business analytics provides valuable insights that enable leaders to make informed choices and develop effective strategies.
2. Improved Efficiency and Performance: Through data analysis, businesses can identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and improve operational efficiency. Analytics helps organizations allocate resources effectively, streamline operations, and enhance overall performance.
3. Customer Understanding and Personalization: Analyzing customer data allows businesses to gain deep insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This knowledge enables personalized marketing efforts, enhanced customer experiences, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Competitive Advantage: Business analytics empowers organizations to stay ahead of the competition by identifying market trends, predicting customer behavior, and making proactive decisions. This enables businesses to capitalize on emerging opportunities and address challenges effectively.
Applicability and Uses of Business Analytics:
Business analytics can be applied to various domains and functions within an organization:
1. Sales and Marketing: Analytics helps optimize marketing campaigns, target the right audience, identify potential customers, and improve sales forecasting. It enables organizations to develop effective pricing strategies, customer segmentation, and personalized marketing campaigns.
2. Operations and Supply Chain: By analyzing data on inventory levels, production rates, and customer demand, organizations can optimize their supply chain, reduce costs, minimize wastage, and improve delivery performance.
3. Finance and Risk Management: Analytics aids in financial planning, budgeting, risk assessment, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. It helps organizations identify potential risks, forecast financial performance, and make informed investment decisions.
4. Human Resources: Analytics can assist in talent acquisition, employee engagement, performance management, and workforce planning. It enables organizations to identify skill gaps, improve retention, and optimize workforce productivity.
Implementation Approach:
Implementing business analytics effectively requires a systematic approach:
1. Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of the analytics initiative. Identify the specific business problems to be solved and the key metrics to measure success.
2. Data Governance and Infrastructure: Establish a robust data governance framework to ensure data quality, security, and accessibility. Invest in appropriate data storage, processing, and analytics tools or platforms.
3. Data Collection and Integration: Collect relevant data from various sources, ensuring its accuracy and consistency. Integrate disparate data sources to create a unified view for analysis.
4. Analytical Techniques and Models: Select appropriate analytical techniques and models based on the specific business problem. This may involve statistical analysis, predictive modeling, machine learning, or a combination of methods.
5. Visualization and Reporting: Present the analysis results in a visually appealing and understandable manner. Utilize data visualization tools to communicate insights effectively to stakeholders.
Best Practices:
To maximize the benefits of business analytics, organizations should follow these best practices:
1. Strong Leadership and Organizational Alignment: Ensure that senior leadership supports and drives the analytics initiative. Align analytics efforts with business objectives and foster a data-driven culture throughout the organization.
2. Skilled Analytics Team: Build a team of skilled data analysts, data scientists, and domain experts. Invest in training and professional development to enhance their analytical capabilities.
3. Agile and Iterative Approach: Adopt an agile approach to analytics projects. Break down larger initiatives into smaller, manageable tasks and iterate based on feedback and changing business needs.
4. Continuous Improvement: Establish a feedback loop to continuously evaluate and improve analytics processes and models. Regularly reassess the relevance and effectiveness of analytics initiatives.
5. Ethical and Responsible Use of Data: Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and ethical guidelines. Safeguard customer data and use it responsibly, ensuring transparency and consent.
Business analytics has become an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to thrive in today's data-driven landscape. By leveraging data to gain insights and make informed decisions, businesses can enhance their competitiveness, improve operational efficiency, and deliver personalized experiences to customers. Through a systematic implementation approach and adherence to best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of business analytics and embark on a journey toward success.
There are numerous tools available in the market that provide business analytics capabilities. Here are some popular ones:
1. Tableau: A widely used data visualization and business intelligence tool that helps in creating interactive dashboards and reports.
2. Power BI: Microsoft's business analytics platform that enables users to visualize and analyze data, create reports, and share insights.
3. QlikView: A data discovery and visualization tool that allows users to explore data and create interactive dashboards.
4. Google Analytics: A web analytics tool that provides insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates.
5. IBM Watson Analytics: An AI-powered analytics platform that enables users to analyze data, build predictive models, and generate visualizations.
6. SAS Analytics: A comprehensive analytics suite offering a wide range of tools for data mining, statistical analysis, and predictive modeling.
7. Apache Hadoop: An open-source framework that facilitates distributed storage and processing of large datasets for advanced analytics.
8. Salesforce Analytics: A cloud-based analytics platform specifically designed for Salesforce users to analyze customer data, sales performance, and marketing campaigns.
9. Domo: A cloud-based platform that integrates data from various sources and provides real-time insights and visualizations.
10. RapidMiner: A data science platform that offers a wide range of analytics tools and features for data preprocessing, modeling, and deployment.
These are just a few examples, and the market offers many more business analytics tools catering to different needs and preferences. Organizations should evaluate their specific requirements and choose the tool that aligns best with their analytics goals and infrastructure.
Here's a comparison of the mentioned business analytics tools, highlighting their pros and cons:
- Tableau:
Pros:
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface for data visualization.
- Wide range of data connectors, making it easy to integrate and analyze various data sources.
- Robust community support and extensive online resources.
- Strong visualization and interactive dashboard capabilities.
Cons:
- Expensive licensing costs for enterprise-level usage.
- Advanced analytics features are limited compared to other tools.
- Large datasets can sometimes lead to performance issues.
- Power BI:
Pros:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft ecosystem, including Excel and SQL Server.
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality for report creation.
- Strong data visualization capabilities and interactive dashboards.
- Extensive sharing and collaboration options.
Cons:
- Limited capabilities for advanced analytics and statistical modeling.
- Lack of support for certain data sources and complex data transformations.
- The steeper learning curve for more complex scenarios.
- QlikView:
Pros:
- Powerful data discovery capabilities for exploring and analyzing data.
- The associative data model allows for dynamic data exploration and intuitive insights.
- Flexible and customizable dashboards and visualizations.
- Strong support for ad-hoc analysis and self-service capabilities.
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve due to a unique scripting language for data modeling.
- Limited support for collaboration and sharing compared to other tools.
- Relatively higher cost compared to some other options.
- Google Analytics:
Pros:
- Comprehensive web analytics platform with a wide range of metrics and insights.
- Easy integration with websites and other Google products.
- Real-time data tracking and reporting.
- Free version available for basic usage.
Cons:
- Limited to web analytics and may not support offline or non-web data analysis.
- Lack of customization options for reporting and visualization.
- Data privacy concerns and reliance on Google's infrastructure.
- IBM Watson Analytics:
Pros:
- Powerful AI-driven analytics capabilities for predictive modeling and data exploration.
- Natural language query interface for easy data exploration and insights.
- Integrated data preparation and cleansing features.
- Strong support for advanced analytics techniques.
Cons:
- Higher learning curve due to the complexity of AI and machine learning concepts.
- Relatively higher pricing for enterprise-level usage.
- Limited customization options for visualizations and dashboards.
It's important to note that these are general pros and cons and may vary based on specific use cases and organizational requirements. Evaluating the features, costs, and suitability for your specific business needs will help in selecting the most appropriate tool.
Wireless Value Realization: Unlocking the Potential of Connectivity

Explore the history, evolution, advancements, and advantages of wireless value realization. Learn about its diverse uses, implementation methodology, and prospects. Discover best practices to leverage wireless technologies for transformative outcomes.
Wireless communication has transformed the way we connect, communicate, and conduct business. From the early days of basic wireless telegraphy to the advent of advanced wireless networks and IoT devices, the evolution of wireless technology has paved the way for wireless value realization. This article delves into the history, evolution, advancements, uses, advantages, implementation methodology, prospects, and best practices associated with wireless value realization.
Wireless value realization refers to the process of deriving tangible benefits and outcomes from wireless technologies and systems. It involves maximizing the value and potential of wireless infrastructure, devices, and applications to achieve specific objectives and deliver positive results.
In the context of wireless communication, value realization can be seen across various domains, such as business, healthcare, transportation, education, and more. Here are some key aspects and considerations related to wireless value realization:
1. Connectivity: Wireless technologies enable seamless connectivity, allowing individuals and devices to stay connected and communicate efficiently. Value realization occurs when this connectivity is leveraged to improve productivity, collaboration, and information sharing. For example, in a business setting, wireless connectivity can enable remote work, real-time data access, and instant communication among team members.
2. Mobility: Wireless networks offer the freedom of mobility, enabling users to access information and services on the go. Value realization involves leveraging this mobility to enhance efficiency and flexibility. For instance, mobile workforce management solutions allow employees to access critical data and applications while working in the field, leading to improved productivity and responsiveness.
3. Internet of Things (IoT): Wireless connectivity is a fundamental enabler of IoT devices, which are interconnected systems collecting and exchanging data. Value realization in the IoT realm involves harnessing wireless networks to enable smart and connected ecosystems. This can result in improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced decision-making through data analytics.
4. Enhanced User Experience: Wireless technologies contribute to delivering enhanced user experiences through faster data speeds, improved reliability, and increased convenience. Value realization occurs when these advantages are utilized to create innovative applications and services that cater to user needs. Examples include immersive virtual reality experiences, mobile payment solutions, and personalized healthcare monitoring through wearables.
5. Cost Efficiency: Wireless value realization also encompasses cost savings and operational efficiencies. For instance, organizations can optimize their operations by implementing wireless sensor networks for monitoring and controlling processes, resulting in reduced energy consumption, predictive maintenance, and improved resource allocation.
6. Innovation and Transformation: By embracing wireless technologies and exploring their potential, businesses and industries can drive innovation and transformation. Value realization involves identifying new business models, revenue streams, and opportunities for growth enabled by wireless connectivity. For example, the rise of 5G networks is expected to unlock possibilities for autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and immersive media experiences.
Wireless value realization involves recognizing and capitalizing on the capabilities offered by wireless technologies to achieve specific objectives, improve efficiency, enhance user experiences, and drive innovation. It requires a strategic approach to maximize the benefits and potential of wireless systems in various domains.
1. History and Evolution:
The foundation of wireless communication can be traced back to the late 19th century when Guglielmo Marconi introduced wireless telegraphy. Over the years, wireless technology has evolved significantly, from analog cellular networks to the digital revolution with the emergence of 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. The latest breakthrough is the deployment of 5G networks, promising unprecedented speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity.
2. Advancements and Uses:
Wireless value realization has found its applications across various sectors. In business, wireless connectivity enables remote work, seamless collaboration, and real-time data access. Healthcare has witnessed the integration of wireless devices for remote patient monitoring and improved healthcare delivery. Transportation systems utilize wireless communication for traffic management, vehicle tracking, and connected cars. Additionally, smart homes, wearables, and IoT devices leverage wireless connectivity for enhanced convenience and automation.
3. Advantages of Wireless Value Realization:
a. Connectivity and Mobility: Wireless networks provide ubiquitous connectivity, enabling users to access information and services on the go. This enhances productivity, flexibility, and responsiveness, leading to improved business outcomes.
b. Cost Efficiency: Wireless value realization offers cost savings through optimized operations, reduced cabling requirements, and improved resource allocation. Wireless sensors and IoT devices can enable predictive maintenance, energy efficiency, and streamlined processes.
c. Enhanced User Experience: Faster data speeds, improved reliability, and convenience provided by wireless technologies result in superior user experiences. Immersive technologies, mobile payments, and personalized applications contribute to enhanced satisfaction and engagement.
4. Implementation Methodology:
To achieve wireless value realization, organizations need to follow a systematic implementation approach:
a. Needs Assessment: Identify the specific objectives, challenges, and requirements that wireless technology can address within the organization.
b. Network Design: Develop a comprehensive plan for deploying wireless infrastructure, considering coverage, capacity, security, and scalability.
c. Device Integration: Integrate wireless-enabled devices and applications to ensure seamless connectivity and interoperability.
d. Security and Compliance: Implement robust security measures to protect data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
e. Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor and optimize the wireless network performance to maximize value realization and address any issues promptly.
5. Future Prospects:
The future of wireless value realization looks promising with the advent of 5G networks, edge computing, and the expansion of IoT ecosystems. These advancements will unlock new possibilities, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, augmented reality, and machine-to-machine communication. The integration of wireless technologies with artificial intelligence and data analytics will further amplify the potential for innovation and transformation.
6. Best Practices:
To achieve optimal wireless value realization, organizations should consider the following best practices:
a. Strategic Planning: Align wireless implementation with organizational goals and develop a long-term roadmap for wireless technology adoption.
b. Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, business units, and stakeholders to ensure that wireless initiatives align with business requirements.
c. Scalability: Design wireless networks with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and technological advancements.
d. Security Focus: Prioritize security measures to protect wireless networks and data, including encryption, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments.
e. Training and Support: Provide training and support to employees to maximize the utilization of wireless technologies and enhance adoption.
Wireless value realization has come a long way since its inception, transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we live and work. The history and evolution of wireless communication have paved the way for advancements that have opened up new opportunities and possibilities. From connectivity and mobility to cost efficiency and enhanced user experiences, the advantages of wireless value realization are far-reaching.
Implementing wireless technologies requires a systematic approach, starting with a needs assessment to identify specific objectives and challenges. Designing a robust wireless network infrastructure, integrating devices and applications, and ensuring security and compliance are crucial steps in the implementation methodology. Continuous monitoring and optimization of network performance are essential to maximize value realization.
Looking toward the future, wireless technology is poised for further growth and innovation. The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster speeds, lower latency, and increased device connectivity, enabling transformative applications and services. Edge computing will bring computing power closer to the source of data, facilitating real-time decision-making and enabling low-latency applications. The expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) will lead to a more connected world, with smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and intelligent systems becoming commonplace.
To make the most of wireless value realization, organizations should adopt best practices. Strategic planning aligns wireless initiatives with business objectives, ensuring a coherent and purposeful implementation. Collaboration between IT, business units, and stakeholders fosters a holistic approach to wireless integration. Scalability considerations accommodate future growth and technological advancements. A strong focus on security safeguards wireless networks and data, protecting against threats. Training and support for employees enhance the adoption and utilization of wireless technologies.
Wireless value realization has a rich history, and its evolution has brought us to an era of unparalleled connectivity and opportunities. By embracing wireless technologies, organizations can unlock the full potential of connectivity, mobility, and innovation. With strategic implementation, adherence to best practices, and a vision for the future, wireless value realization will continue to shape and transform industries, delivering tangible benefits and outcomes for individuals and businesses alike.
A Digitally Edible World: Exploring the Current Status, Evolution, Applicability, and Future Possibilities

In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, the integration of digital innovations into various aspects of our lives is becoming increasingly prevalent. One fascinating area where this convergence is taking place is in the realm of food and dining. Welcome to the era of a digitally edible world, where technology is revolutionizing the way we experience, interact with, and even consume our meals. In this article, we will delve into the current status, evolution, applicability, and future possibilities of this exciting concept.
A digitally edible world refers to a concept where digital technology is integrated into the food and beverage industry in innovative and interactive ways. It involves the use of digital elements to enhance and transform the way we experience and interact with food.
In a digitally edible world, various technologies are employed to create immersive and engaging dining experiences. This can include augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications that overlay digital information or virtual environments onto real-world dining settings. For example, using AR glasses or a smartphone app, diners could see digital images or animations appearing on their plates or hovering above the table, adding an interactive and visual element to their meals.
Another aspect of a digitally edible world is the use of edible electronics or food-based sensors. These technologies involve embedding electronic components or sensors into food items or packaging materials. They can provide real-time information about the food's freshness, and nutritional content, or even tailor the taste according to personal preferences. For instance, edible sensors could detect a person's dietary restrictions or allergies and adjust the composition of the food accordingly.
Additionally, digital platforms and applications can be used to enhance the entire food ecosystem, including aspects such as food sourcing, delivery, and sharing experiences. These platforms can connect consumers with local farmers, promote sustainable farming practices, and enable seamless online ordering and delivery services. Social media platforms could also play a role in sharing food experiences, recipes, and recommendations within a digitally connected community.
A digitally edible world envisions a future where technology and food converge to create new and exciting possibilities for dining experiences, personalized nutrition, and sustainable food systems. It aims to revolutionize the way we interact with food, making it more engaging, informative, and enjoyable.
The concept of a digitally edible world is gaining traction across the globe. We are witnessing the emergence of numerous technologies that aim to transform our dining experiences. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications are being developed to overlay digital content onto real-world dining settings, providing interactive and immersive experiences for consumers. From visual effects on plates to virtual dining environments, these technologies are already making their way into restaurants and culinary events, captivating diners with a fusion of the digital and gastronomic worlds.
The evolution of a digitally edible world has been driven by advancements in various fields. The miniaturization of electronics and the rise of wearable devices have opened up possibilities for embedding sensors and components directly into food items or packaging. Edible electronics and food-based sensors can provide real-time information about the food's quality, freshness, and nutritional content, enabling consumers to make informed choices. These technologies are still in their early stages but hold tremendous potential for shaping the future of food.
The applicability of a digitally edible world spans multiple domains within the food industry. Restaurants and culinary establishments can leverage augmented reality to enhance the dining experience, offering interactive menus, visual presentations of dishes, or even storytelling elements related to the food's origins and preparation. Online food delivery services can benefit from digital platforms that optimize logistics and enable real-time tracking, ensuring efficient and timely delivery. Additionally, personalized nutrition and dietary management can be facilitated through the use of sensors that monitor individuals' specific needs and tailor food composition accordingly.
Looking ahead, the future of a digitally edible world holds boundless potential. Imagine a scenario where personalized holographic chefs guide home cooks through recipes, or where 3D-printed food items with customized flavors and textures become commonplace. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, we can anticipate more sophisticated applications in food production, supply chain management, and sustainability efforts. Additionally, the power of social media and online platforms will further amplify the sharing of culinary experiences, enabling food enthusiasts to connect, collaborate, and learn from one another on a global scale.
A digitally edible world is gradually becoming a reality, blending the realms of technology and gastronomy in fascinating ways. With ongoing advancements and the increasing integration of digital innovations into the food industry, we are poised for a future where dining experiences are more engaging, interactive, and personalized than ever before. From augmented reality and edible sensors to personalized nutrition and digital platforms, the possibilities are vast. As we embark on this transformative journey, it is essential to balance technological advancements with sustainability, ethics, and the preservation of traditional culinary arts. Together, let us savor the flavors of a digitally edible world while embracing the rich tapestry of our food culture.
Demystifying the Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Ensuring Transparency and Accountability in Financial Reporting
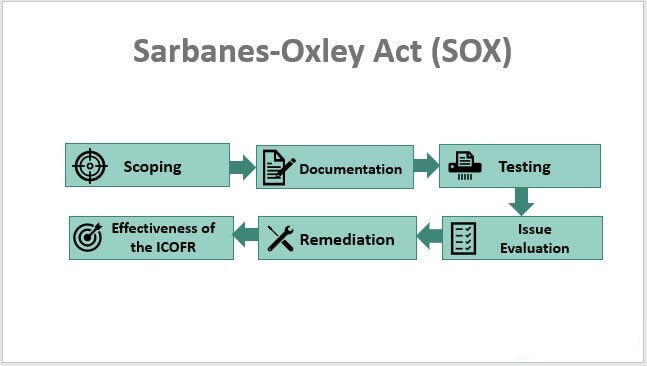
Learn about the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), a vital legislation designed to foster honesty and transparency in corporate financial reporting. This article provides a simplified overview of SOX, its objectives, and the key requirements it imposes on companies to protect investors and restore public confidence.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) is a law created to make sure that companies are honest and transparent in their financial reporting. It was put in place after some big companies were found to be involved in accounting scandals that hurt investors.
SOX has a few main goals:
- Financial Disclosures: Companies must provide accurate and reliable information about their finances to the public. This helps investors make informed decisions.
- Internal Controls: Companies need to have strong systems and processes in place to prevent fraud and errors in their financial reports. They must regularly evaluate these controls to ensure they are effective.
- Auditor Independence: Auditors, the people who check a company's financial records, need to be independent and unbiased. They are not allowed to provide certain non-audit services to the same company they are auditing.
- Whistleblower Protection: Employees who report illegal or unethical activities within their companies are protected under SOX. This encourages a culture of honesty and accountability.
To comply with SOX, companies need to follow best practices, such as:
- Demonstrating a commitment to compliance from top management.
- Assessing and managing risks related to financial reporting.
- Documenting and testing internal controls to ensure they work properly.
- Providing training and communication to employees about their responsibilities.
- Engaging external auditors to review the company's financial processes.
- Keeping records and documentation of compliance activities.
Complying with SOX helps companies build trust with investors and protects them from financial fraud. It ensures that companies are transparent, and accountable, and act in the best interests of their shareholders.
Understanding the Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Applications, Creation, Best Practices, and Implementation Approach
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) is a crucial piece of legislation enacted in the United States in 2002 to protect investors and restore public confidence in the financial markets. Named after its sponsors, Senator Paul Sarbanes and Representative Michael Oxley, the Act introduced significant reforms to corporate governance, financial reporting, and auditing practices. This article will provide an overview of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, its applications, the reasons behind its creation, best practices for compliance, and a recommended implementation approach.
- Applications of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act: The Sarbanes-Oxley Act applies to all publicly traded companies, both domestic and foreign, that are listed on U.S. stock exchanges. Its provisions impact various aspects of corporate governance, financial reporting, and auditing, including:
a) Enhanced Financial Disclosure: Companies are required to disclose accurate and reliable financial information to the public, ensuring transparency and accountability.
b) Internal Controls: SOX mandates the establishment and evaluation of internal controls to mitigate the risk of financial fraud and misstatements. This includes regular assessment of control effectiveness and reporting of any identified deficiencies.
c) Auditor Independence: The Act restricts auditors from performing certain non-audit services for the same client, reducing potential conflicts of interest and enhancing auditor independence.
d) Whistleblower Protection: SOX protects employees who report fraudulent activities within their organizations, encouraging a culture of accountability and integrity.
- Reasons for Creation: The Sarbanes-Oxley Act was enacted in response to high-profile corporate accounting scandals, such as Enron and WorldCom, which severely damaged investor confidence. The Act aimed to address the following key concerns:
a) Financial Fraud and Mismanagement: SOX sought to prevent fraudulent activities by imposing stricter regulations and increasing the accountability of corporate executives and auditors.
b) Inadequate Corporate Governance: The Act aimed to improve corporate governance practices, ensuring that boards of directors and management fulfill their fiduciary duties and act in the best interests of shareholders.
c) Weak Internal Controls: SOX aimed to strengthen internal control systems within companies to prevent financial misstatements and fraudulent practices.
- Best Practices for Compliance: To effectively comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, organizations should consider the following best practices:
a) Top-Down Commitment: Management should demonstrate a strong commitment to compliance, establishing a culture of ethical behavior and accountability throughout the organization.
b) Risk Assessment: Conduct regular assessments to identify and prioritize potential risks and areas of non-compliance, allowing for the implementation of appropriate internal controls.
c) Documentation and Testing: Maintain comprehensive documentation of internal controls and regularly test their effectiveness to identify any weaknesses or deficiencies.
d) Training and Communication: Provide ongoing training to employees regarding their responsibilities, the Act's requirements, and the organization's policies and procedures. Foster open lines of communication for reporting potential issues or concerns.
- Implementation Approach: When implementing Sarbanes-Oxley compliance, organizations should consider the following approach:
a) Awareness and Education: Educate stakeholders about the Act's requirements, implications, and the need for compliance.
b) Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's financial reporting and internal control systems to identify gaps and potential risks.
c) Design and Implementation: Develop and implement robust internal controls, policies, and procedures tailored to the organization's specific needs and risks.
d) Testing and Monitoring: Regularly test and monitor the effectiveness of internal controls, ensuring they operate as intended and promptly address any identified deficiencies.
e) Continuous Improvement: Establish a process for ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and enhancement of the organization's compliance efforts to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and emerging risks.
f) External Audit: Engage an independent external auditor to assess the effectiveness of the organization's internal controls and financial reporting processes. This ensures an objective evaluation and provides additional assurance to stakeholders.
g) Documentation and Recordkeeping: Maintain detailed documentation of compliance activities, including policies, procedures, testing results, and audit reports. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance and facilitates future audits.
h) Remediation of Deficiencies: Promptly address any identified control deficiencies or non-compliance issues through remediation plans. Regularly review and update these plans to ensure effectiveness.
i) Board Oversight: Establish a governance structure that includes active oversight by the board of directors or an audit committee to monitor compliance efforts and provide guidance and support.
j) Regular Reporting: Prepare and submit required reports and disclosures accurately and promptly to regulatory authorities, shareholders, and other stakeholders.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act plays a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity of financial reporting and restoring public confidence in the corporate world. By establishing stringent regulations, enhancing transparency, and strengthening internal controls, the Act aims to prevent financial fraud and mismanagement. Adhering to best practices and following a systematic implementation approach enables organizations to effectively comply with SOX requirements and create a culture of ethical behavior and accountability. Compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act not only ensures legal obligations but also contributes to the long-term success and sustainability of organizations in today's complex business landscape.
HIPAA: Protecting Your Health Information in the Digital Age
In an era where personal health information is increasingly stored and transmitted electronically, it is crucial to understand and comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). This article explores the applications, origins, best practices, and implementation approaches of HIPAA, highlighting its significance in safeguarding sensitive health data.
HIPAA, which stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a law in the United States that helps protect people's personal health information. It was created to make sure that healthcare providers and others who handle this information keep it safe and private.
HIPAA has a few important parts. One part is called the Privacy Rule, which says that healthcare providers and organizations must keep their health information private and only use it for necessary purposes. They can't share it with others without your permission, except in certain situations like emergencies or when required by law.
Another part is the Security Rule, which focuses on electronic health information. It requires healthcare providers to have safeguards in place to protect this information from unauthorized access or hacking. They need to use things like secure computer systems and encryption to keep their electronic health information safe.
HIPAA also has rules about what happens if there is a data breach, which means your health information is accidentally or intentionally accessed by someone who shouldn't have it. In such cases, the healthcare provider must notify you and take steps to fix the situation.
To follow HIPAA, healthcare providers, and organizations need to have policies and procedures in place to protect their information. They should train their employees on how to handle health information properly and securely. They also need to regularly review their systems, identify any risks, and take action to fix them.
HIPAA is important because it ensures that your personal health information is treated with care, kept private, and protected from unauthorized access. It gives you more control over how your health information is used and helps maintain trust between patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding HIPAA: Applications, Origins, Best Practices, and Implementation Approach
In an increasingly digital world where personal health information is stored, transmitted, and accessed electronically, protecting the privacy and security of patient data is of paramount importance. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a vital legislation in the United States that sets standards and safeguards for safeguarding sensitive health information. In this article, we will delve into the applications of HIPAA, its origins, best practices, and implementation approaches.
- Applications of HIPAA: HIPAA serves as a comprehensive framework for protecting health information across various entities, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses. Its key applications are as follows:
a) Privacy Rule: The HIPAA Privacy Rule establishes national standards to protect individuals' medical records and other personal health information. It defines the permitted uses and disclosures of protected health information (PHI) and grants individuals certain rights regarding their health information.
b) Security Rule: The HIPAA Security Rule complements the Privacy Rule by outlining specific safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic PHI (ePHI). It requires covered entities to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect against unauthorized access, use, and disclosure of ePHI.
c) Breach Notification Rule: This rule mandates covered entities to notify affected individuals, the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media, in the event of a breach compromising unsecured PHI. It aims to promptly inform individuals and take necessary actions to mitigate potential harm.
- Origins of HIPAA: HIPAA was enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1996 to address the evolving healthcare landscape, promote efficiency, and safeguard patient privacy. Its primary goals are to improve the portability and continuity of health insurance coverage, combat fraud and abuse in the healthcare system, and protect sensitive health information.
- Best Practices for HIPAA Compliance: To ensure compliance with HIPAA, organizations handling PHI should adhere to the following best practices:
a) Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment: Perform regular assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and risks to PHI's confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This assessment helps organizations develop appropriate safeguards and implement necessary security measures.
b) Develop and implement policies and procedures: Establish clear policies and procedures that address the handling of PHI, including access controls, encryption, data retention, employee training, and incident response. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect technology, regulations, and organizational needs changes.
c) Train employees: Conduct ongoing training sessions for employees to create awareness about HIPAA requirements, the importance of data privacy, and the organization's specific policies and procedures. Employees should be well-informed about their roles and responsibilities in protecting PHI.
d) Encrypt and secure electronic communications: Implement strong encryption mechanisms for ePHI during transmission and storage. This includes secure email systems, virtual private networks (VPNs), and secure file transfer protocols (SFTPs). Apply access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel only.
e) Maintain audit trails and monitor system activity: Regularly review and analyze system logs, audit trails, and access records to detect any suspicious or unauthorized activity. Implement real-time monitoring, intrusion detection, and incident response mechanisms to promptly address potential breaches.
- Implementation Approach: Implementing HIPAA compliance requires a holistic approach, involving the following steps:
a) Establish a compliance team: Designate a dedicated team or individual responsible for overseeing HIPAA compliance efforts. This team should include representatives from different departments, such as IT, legal, privacy, and security.
b) Conduct a gap analysis: Evaluate existing policies, procedures, and technical infrastructure against HIPAA requirements. Identify gaps and prioritize remediation efforts based on risk factors and potential impact on the security of PHI.
c) Develop a comprehensive compliance program: Based on the gap analysis, create a tailored compliance program that aligns with HIPAA regulations. This program should include policies, procedures, and guidelines addressing privacy, security, breach notification, and employee training.
d) Implement technical safeguards: Deploy necessary technical measures to protect ePHI, such as firewalls, encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. Regularly update and patch software systems to address vulnerabilities and stay protected against emerging threats.
e) Train and educate employees: Provide regular training sessions to employees on HIPAA requirements, security best practices, and the organization's specific policies. Employees should understand the importance of data privacy and their role in safeguarding PHI.
f) Establish business associate agreements: If the organization works with third-party vendors or contractors who handle PHI, ensure that appropriate business associate agreements (BAAs) are in place. These agreements should outline the responsibilities and obligations of the business associates regarding PHI protection.
g) Conduct regular risk assessments and audits: Continuously monitor and assess the effectiveness of the implemented safeguards and controls. Regularly conduct internal audits and risk assessments to identify areas of improvement and address any vulnerabilities or non-compliance issues.
h) Incident response and breach management: Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident or data breach. Establish a clear protocol for reporting, investigating, and mitigating breaches, and ensure compliance with breach notification requirements.
i) Maintain documentation: Keep thorough records of all compliance activities, including policies, procedures, training sessions, risk assessments, and incident response plans. Documentation serves as evidence of the organization's commitment to compliance and can be valuable in audits or investigations.
j) Stay updated with regulatory changes: Stay informed about updates to HIPAA regulations and other relevant industry standards. Regularly review and update the compliance program to ensure ongoing alignment with changing requirements.
In conclusion, HIPAA plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive health information in the digital age. Understanding its applications, origins, and best practices is essential for healthcare organizations and other entities handling PHI. By adopting a proactive approach to HIPAA compliance, organizations can protect patient privacy, maintain trust, and mitigate potential risks associated with the handling of sensitive health information.
Understanding Computing Power: Computation, Optimization, and Requirements
Computing power plays a vital role in today's technology-driven world. It determines the efficiency and performance of applications, from simple tasks like web browsing to complex calculations in artificial intelligence and scientific research. In this article, we will explore what computing power is, how it is computed, how to optimize it, and how to derive the required computing power for any application.
What is Computing Power?
Computing power refers to the capability of a system to perform calculations and process information. It is typically measured in terms of the number of calculations a computer can perform per second, often expressed in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS). Computing power is determined by factors such as the speed of the processor, the number of processors, and the efficiency of the algorithms employed.
Computing Power Computation: The computation of computing power depends on various hardware and software components. The primary component is the central processing unit (CPU), which executes instructions and performs calculations. The clock speed of the CPU, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines the number of instructions it can execute per second. Additionally, the number of cores in a CPU affects the parallel processing capabilities and overall computing power.
To calculate the total computing power of a system, multiply the clock speed by the number of cores and the number of instructions per clock cycle. For example, a quad-core CPU with a clock speed of 3.5 GHz and 4 instructions per clock cycle would yield a computing power of 56 GFLOPS (3.5 GHz × 4 instructions/cycle × 4 cores).
Optimizing Computing Power: Optimizing computing power involves maximizing the efficiency of hardware and software components to achieve faster and more accurate computations. Here are some strategies for optimizing computing power:
1. Efficient Algorithms: Choosing or designing algorithms that require fewer computations or utilize parallel processing can significantly improve performance.
2. Hardware Upgrades: Upgrading components like the CPU, increasing the number of cores, or utilizing specialized hardware like graphics processing units (GPUs) for parallel processing can boost computing power.
3. Memory Management: Optimizing data storage and retrieval processes, such as caching frequently accessed data, can reduce processing time and improve overall performance.
4. Parallelization: Breaking down tasks into smaller subtasks that can be executed simultaneously across multiple cores or machines can leverage parallel processing and speed up computations.
5. Code Optimization: Writing efficient and optimized code, eliminating redundant calculations, reducing memory usage, and using compiler optimizations can lead to substantial performance gains.
Deriving Required Computing Power: Determining the required computing power for an application depends on several factors, including the nature of the task, its complexity, and performance expectations. Here are steps to derive the required computing power:
1. Task Analysis: Understand the computational requirements of the application. Determine if it involves heavy calculations, simulations, data processing, or requires real-time responsiveness.
2. Benchmarking: Conduct benchmark tests on representative workloads to measure the performance of the application on different hardware configurations. This helps identify the required computing power to meet desired performance goals.
3. Scalability Considerations: If the application needs to handle increasing workloads or larger datasets, consider the scalability requirements and ensure that computing power can handle future growth.
4. Consultation and Research: Seek expert advice, consult software developers, or refer to the documentation and online resources to understand the recommended computing power for similar applications.
5. Cost Optimization: Balance the required computing power with cost considerations. Choose a configuration that meets the application's needs while being cost-effective and scalable.
Computing power is a fundamental aspect of modern technology and impacts the performance of various applications. By understanding how computing power is computed, optimizing it through efficient algorithms and hardware upgrades, and deriving the required
Understanding the Different Types of Information Systems: Applications, Best Practices, and Implementation Approach
In today's business landscape, information systems are a critical component of efficient and effective operations. From transaction processing systems to customer relationship management, there are various types of information systems. Each has its unique purpose, applications, best practices, and implementation approach. In this article, we will explore the different types of information systems, their uses, and how to implement them effectively.
Information systems (IS) are a vital part of modern-day businesses. They provide the necessary tools and resources to effectively manage and process data and information. There are different types of information systems, each with its unique application, best practices, and implementation approach. In this article, we will explore the various types of information systems, their applications, best practices, and implementation approach.
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): Transaction processing systems are designed to process large volumes of data generated from day-to-day business transactions. They are commonly used in businesses that handle a large number of transactions, such as retail stores, banks, and airlines. TPS is responsible for capturing, processing, and storing data related to transactions. The primary purpose of TPS is to ensure that transactions are processed accurately and promptly.
Best Practices for TPS
- Ensure that data is validated and accurate before processing.
- Implement backup and recovery mechanisms to ensure data is not lost in case of system failure.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Implementation approach
- Analyze business processes and identify the types of transactions that need to be captured.
- Identify the types of data that need to be captured and stored.
- Develop a data model and design the TPS to capture and process data.
- Management Information Systems (MIS): Management information systems are designed to provide management with information necessary for decision-making. MIS is used to analyze and summarize data generated by other information systems. The primary purpose of MIS is to provide management with information that helps them make informed decisions.
Best Practices for MIS
- Ensure that the information provided is accurate and up-to-date.
- Provide easy-to-use interfaces for managers to access information.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Implementation approach
- Identify the types of information that management requires to make informed decisions.
- Develop a data model and design the MIS to provide the necessary information.
- Integrate MIS with other information systems to ensure data consistency.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): Decision support systems are designed to support decision-making processes by providing data analysis and modeling tools. DSS is used to analyze data and help users make informed decisions based on the results of data analysis.
Best Practices for DSS
- Ensure that the data used for analysis is accurate and up-to-date.
- Provide easy-to-use interfaces for users to access data analysis tools.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Implementation approach
- Identify the types of decisions that need to be made.
- Identify the data required for decision-making.
- Develop data analysis and modeling tools that can be used to support decision-making processes.
- Expert Systems: Expert systems are designed to mimic the decision-making processes of human experts. They use knowledge-based rules to provide advice and recommendations to users. Expert systems are commonly used in areas where expertise is required, such as healthcare, law, and finance.
Best Practices for Expert Systems
- Ensure that the knowledge base used for decision-making is accurate and up-to-date.
- Provide easy-to-use interfaces for users to access expert systems.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Implementation approach
- Identify the types of decisions that require expertise.
- Identify the types of knowledge required for decision-making.
- Develop the knowledge base and rules that can be used to support decision-making.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Enterprise resource planning systems are designed to integrate different business functions and provide a single view of business operations. ERP systems are commonly used in large organizations that have complex business processes.
Best Practices for ERP
- Ensure that data used in ERP is accurate and up-to-date.
- Implement backup and recovery mechanisms to ensure data is not lost in case of system failure.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Implementation approach
- Identify the business functions that need to be integrated.
- Develop a data model and design the ERP system to integrate the different business functions.
- Integrate the ERP system with other information systems to ensure data consistency.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Customer relationship management systems are designed to manage and analyze interactions with customers. CRM systems are commonly used in businesses that have a large customer base, such as banks, insurance companies, and e-commerce websites.
Best Practices for CRM
- Ensure that customer data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Provide easy-to-use interfaces for customer interaction.
- Implement security measures to prevent unauthorized access to customer data.
Implementation approach
- Identify the types of interactions that need to be managed.
- Develop a data model and design the CRM system to manage customer interactions.
- Integrate the CRM system with other information systems to ensure data consistency.
Information systems are an essential component of modern-day businesses. They provide businesses with the necessary tools and resources to manage and process data effectively. There are different types of information systems, each with its unique application, best practices, and implementation approach. Understanding the different types of information systems and their applications can help businesses make informed decisions when implementing information systems. By following best practices and appropriate implementation approaches, businesses can ensure that their information systems are accurate, reliable, and secure.
Cybersecurity on a Budget: How Small Businesses Can Stay Secure with Limited Resources

In today's digital age, cybersecurity is crucial for small businesses. However, with limited resources, it can be challenging to implement effective cybersecurity measures. This article will provide insights into how small businesses can set up an affordable and comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
As technology becomes more prevalent in the business world, the threat of cyber attacks is increasing rapidly. While large corporations have the resources to invest heavily in cybersecurity, small businesses often have limited resources to protect themselves. However, effective cybersecurity doesn't have to be expensive. There are several steps small businesses can take to protect themselves on a budget.
Step 1: Create a Cybersecurity Plan
The first step in protecting your business from cyber attacks is to create a cybersecurity plan. This plan should outline the steps you will take to protect your business, including the tools and processes you will use. The plan should also include details on how you will respond to a cyber attack.
Step 2: Train Your Employees
Your employees are your first line of defense against cyber attacks. Therefore, it's important to train them on how to identify and respond to potential threats. This can include training on how to create strong passwords, how to identify phishing emails, and how to avoid downloading malicious software.
Step 3: Use Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is a crucial component of any cybersecurity plan. This software can help protect your business from malware and other types of cyber attacks. While there are many different antivirus products on the market, some good options for small businesses on a budget include Avast, AVG, and Microsoft Defender.
Step 4: Implement Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a simple but effective way to protect your business from unauthorized access. This process requires users to provide two forms of identification before they can access sensitive information. Many online services now offer two-factor authentication, including Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn.
Step 5: Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A virtual private network (VPN) can help protect your business from cyber attacks by encrypting your online traffic. This can help prevent hackers from intercepting your data and accessing your sensitive information. Some good VPN options for small businesses on a budget include TunnelBear and Hotspot Shield.
Step 6: Backup Your Data
Backing up your data is an essential part of any cybersecurity plan. This can help protect your business from data loss in the event of a cyber attack. Some good backup solutions for small businesses on a budget include Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
Step 7: Monitor Your Network
Monitoring your network is an important part of any cybersecurity plan. This can help you detect potential threats before they become a problem. Some good network monitoring tools for small businesses on a budget include PRTG Network Monitor and Spiceworks Network Monitor.
Cybersecurity is a critical concern for small businesses, but it doesn't have to be expensive. By creating a cybersecurity plan, training your employees, using antivirus software, implementing two-factor authentication, using a VPN, backing up your data, and monitoring your network, you can effectively protect your business from cyber-attacks. With these simple steps and affordable products, even small businesses can implement effective cybersecurity measures.
Here's a list of cybersecurity products that small businesses can consider using, along with their advantages and disadvantages:
- Antivirus Software:
a. Avast: Avast offers a free antivirus solution for small businesses with basic features such as virus scanning, firewall protection, and email security.
b. AVG: AVG is another free antivirus solution that offers similar features to Avast.
c. Microsoft Defender: Microsoft Defender is a built-in antivirus software that comes with Windows 10 and provides real-time protection against viruses, spyware, and other malicious software.
Advantages:
- These antivirus products are affordable or free for small businesses.
- They provide essential protection against viruses, malware, and other cyber threats.
Disadvantages:
- Free versions may have limited features and capabilities.
- They may not provide comprehensive protection against more sophisticated cyber attacks.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN):
a. TunnelBear: TunnelBear offers a free VPN solution for small businesses with basic features such as data encryption and protection from online tracking.
b. Hotspot Shield: Hotspot Shield provides a VPN solution that offers high-speed browsing and strong encryption.
Advantages:
- VPNs encrypt online traffic, protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
- They can provide access to geo-blocked content and protect against public Wi-Fi risks.
Disadvantages:
- Free VPNs may have limited bandwidth and features.
- Some VPNs may slow down the internet speed.
- Two-Factor Authentication:
a. Google Authenticator: Google Authenticator provides a two-factor authentication solution that is free to use and compatible with most online services.
b. Microsoft Authenticator: Microsoft Authenticator is a free app that provides two-factor authentication for Microsoft services.
Advantages:
- Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to online accounts.
- Many online services now offer two-factor authentication.
Disadvantages:
- Two-factor authentication may cause inconvenience to users.
- Backup Solutions:
a. Dropbox: Dropbox offers a cloud-based backup solution that provides automatic backup and file syncing across devices.
b. Google Drive: Google Drive is a free backup solution that provides cloud storage and file sharing.
Advantages:
- Backup solutions can prevent data loss in the event of a cyber attack or hardware failure.
- Cloud-based solutions offer remote access to data.
Disadvantages:
- Free versions may have limited storage capacity.
- Cloud-based solutions may be vulnerable to hacking and data breaches.
- Network Monitoring Tools:
a. PRTG Network Monitor: PRTG Network Monitor provides network monitoring and analysis tools that help detect network issues and cyber threats.
b. Spiceworks Network Monitor: Spiceworks Network Monitor offers real-time network monitoring and alerting for small businesses.
Advantages:
- Network monitoring tools can help detect and prevent cyber threats before they cause damage.
- They can identify network issues and provide insights into network performance.
Disadvantages:
- Network monitoring tools may be complex to set up and use.
- They may require additional hardware or software for effective use.
These cybersecurity products offer affordable and effective protection for small businesses. While each product has its advantages and disadvantages, the key is to find the right combination of tools that meets your business needs and budget.
Implementing the cybersecurity solutions mentioned in this article requires a combination of technical and non-technical skills. Here are some essential skills that may be required:
- Technical skills:
- Knowledge of computer networks, operating systems, and security protocols.
- Familiarity with cybersecurity tools and software.
- Proficiency in configuring and troubleshooting software and hardware systems.
- Understanding of cloud-based solutions and data backup processes.
- Communication skills:
- Ability to communicate technical information to non-technical stakeholders.
- Strong written and verbal communication skills to interact with team members and clients.
- Analytical skills:
- Ability to analyze network traffic and system logs to identify potential security threats.
- Attention to detail to identify vulnerabilities in the system.
- Time management skills:
- Ability to prioritize tasks and manage time efficiently to meet project deadlines.
- Ability to work under pressure and in a fast-paced environment.
- Continuous learning:
- Willingness to keep up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity threats and technologies.
- Interest in improving and expanding technical knowledge and skills.
In summary, implementing cybersecurity solutions requires a combination of technical and non-technical skills. It is essential to have a team member or partner with the necessary expertise to ensure that the implementation is successful and effective.
The decision to outsource or in-source the implementation of cybersecurity solutions for small businesses ultimately depends on the available resources, budget, and expertise. Here are some factors to consider:
1. In-sourcing: If the small business has employees with the necessary technical skills and expertise to implement cybersecurity solutions, in-sourcing may be a viable option. In-sourcing allows the business to have complete control over the implementation process, ensuring that the solutions align with the business's specific needs and goals.
Advantages:
- Complete control over the implementation process.
- Ability to customize the solutions to meet the business's specific needs.
- Opportunity to upskill existing employees in cybersecurity.
Disadvantages:
- It may require additional resources and time to train existing employees.
- It may take away valuable time and resources from other business operations.
2. Outsourcing: Outsourcing the implementation of cybersecurity solutions can provide small businesses with access to specialized expertise and technologies that may not be available in-house. It allows businesses to focus on their core operations while leaving cybersecurity implementation to experts.
Advantages:
- Access to specialized expertise and technologies.
- Reduced workload on in-house employees, allowing them to focus on core operations.
- Access to cost-effective solutions.
Disadvantages:
- Less control over the implementation process.
- Potential communication and coordination issues with the outsourced vendor.
In conclusion, the decision to outsource or in-source the implementation of cybersecurity solutions for small businesses depends on the available resources, budget, and expertise. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach is to consider these factors and make an informed decision that aligns with the business's specific needs and goals.
In conclusion, small businesses can set up an affordable and effective cybersecurity strategy to protect their sensitive data and prevent cyber threats, even with limited resources. By following the steps outlined in this article, such as investing in antivirus software, implementing two-factor authentication, using a VPN, and deploying network monitoring tools, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture.
It is also important to note that implementing cybersecurity solutions requires a combination of technical and non-technical skills. Small businesses can either outsource or in-source the implementation of cybersecurity solutions, depending on their resources, budget, and expertise.
Small businesses must prioritize cybersecurity to protect their data and maintain customer trust. By taking proactive measures to secure their networks and systems, small businesses can avoid the high costs associated with data breaches and other cybersecurity incidents.
Ultimately, with the right approach, tools, and skills, small businesses can effectively mitigate cybersecurity risks and focus on growing their business without worrying about security threats.
Nokia: From Wood Mill to Mobile Behemoth - A Journey of Innovation and Adaptation

From wood mill to mobile behemoth: Learn about Nokia's fascinating journey from its humble origins in Nokia City, Finland to becoming a global leader in the mobile phone industry, and the importance of innovation, adaptation, and diversification in business.
Nokia, one of the most well-known mobile phone brands today, has an interesting history that dates back to its origins as a wood mill in Nokia City, Finland.
Nokia started as a wood mill in Nokia City, Finland before venturing into the rubber products industry and eventually becoming a famous mobile behemoth. Learn about Nokia's journey and the importance of innovation, adaptation, and diversification in business.
It's interesting to note the humble beginnings of Nokia as a wood mill in Finland and its transition into the rubber products segment before becoming the well-known mobile behemoth it is today. Nokia's evolution into different industries reflects its adaptability and willingness to innovate, which has been a key factor in its success over the years.
It also highlights the importance of diversification in business, as Nokia's ventures into various industries allowed the company to stay relevant and profitable over time. This is a valuable lesson for other companies looking to sustain their growth and success in the long run.
Nokia's history serves as an inspiration for aspiring entrepreneurs and a testament to the power of innovation, adaptation, and diversification in business.
These Interesting Facts About Nokia Will Surprise You!
Lately, the world has graduated from the playschool era. Pigeons are now substituted with a gadget called 'Mobile'. The stakeholders keep on trying to evolve and lurch past the pace of the cosmos. In the meantime, there are a lot of things that came into the limelight after someone or the other discovered them.
One such profound discovery is the mobile phone. Nowadays most commonly known as a smartphone, was first discovered in 1973 in its basic form. The model was not a lot smart but was like a well amid a desert.
Nokia is one such company that is famous worldwide for its range of mobile phones. Nokia's products were like a wand of magic for the former generation of people. It is one of those very few companies which helped people connect sitting far away from each other. So let us today have a look at some wonderful facts about the company which was loved the most by our father generation. But before we savor the delicious facts, let us just have a brief glimpse of the company's highlights.
Interesting Facts about Nokia
Now, let us dive deeper into the facts that we have mentioned just above. Knowing about the details is going to be a really fun activity now and we hope you get amazed by every sub-point.
Origin
The company took its very first breath in the year 1865. There is a slight twist here though. The company didn't start as a mobile-producing giant. It was instead a paper mill. The company produced paper pulp in Finland. Fredrik Idestam had set up this factory then. After a few years in 1871, with the help of his friend Leo Mechelin, the paper pulp company transformed into a share company. After that, the name Nokia came into the market.
Naming
- The company was built on the bank of the Nokianvirta River and that's why the founders named it Nokia.
- Nokia was established as a pulp mill on the shore of Tammerkoski. It has other branches like Nokia rubber boots and cable works and in modern times Nokia is famous for its durable mobile phones. These branches together formed the Nokia cooperation.
- Many people must have heard about the famous guitar work named 'Gran Vals' of the 19th century. It was done by a Spanish musician Francisco Tarrega. From here the tune arrived for Nokia in 1999.
- It is a very common belief in most parts of Asia that the number 04 resembles the sound of absolute death. The production team of Nokia keeps the same in mind and till now has not made a single model of Nokia which starts from the number 04.
- When we talk about the first phone without an external antenna attached to the phone, it's too obvious that model 8810 of Nokia comes flashing in front of the eye. It was the first Nokia set that had no external antenna to it. It was launched in 1998 and was the most luxurious mobile back then. Adding more spices to it, it also had chrome plating.
- Nokia 3310 is no less than Thanos of Avengers. It is more commonly and widely known as the 'Unbreakable phone' of history. It had the best durability back then. The fun fact is that people used to throw their phones with loud confidence to show off their durability.
- In Helsinki city of Finland on 1st July 1991, the world's first GSM phone call was made. The call was made by the honorable prime minister of Finland, Mr. Harris Holkeri using a model of the Nokia company.
- Every child wishes to get a phone which has a pre-installed game, which they can play without spending a dollar. Nokia 6110 was the dream-come-true set for game lovers. It came with a pre-installed snake game which became very popular and was loved by all and is still missed by many people who were once a child back then.
- The first camera phone from the Nokia House came in the year 2002 its model number is 7650. Though it only had a camera of 0.3 megapixels.
- It is a very interesting fact that the SMS tone of Nokia is a Morse code that is used for 'connecting people and SMS'.
- As per a list of 2006 survey, Nokia was the 20th most admirable company in the world.
- As per the last calculation in the year 2019, Nokia had a net worth of 15.4 billion euros.
- The
achievements and awards of Nokia are listed below -
- World's most ethical company in 2021 by Ethisphere
- National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences in 2020
- Best secured network initiative in 2019
- Nokia 9 is the till date best model of Nokia with 5 cameras and a decent processor.
Nokia has been one of the best mobile-producing companies in the world along with other branches of it. It has always stood on the expectations and is best known for its camera features. The people of the 90s still brag about how they used to use Nokia phones back then. Nokia is not just a company but is an emotion for its regular users.
The Advanced Scientific Knowledge in Ancient Indian Scriptures: A Look at Modern Discoveries

The ancient Indian scriptures contain a wealth of knowledge and wisdom that has fascinated scholars and researchers for centuries. In recent years, modern science has been able to confirm many of the scientific facts mentioned in these texts, highlighting the advanced understanding of the natural world that existed in ancient India.
Ancient Indian scriptures, including the Vedas, Upanishads, and Puranas, are renowned for their rich philosophical and spiritual insights. However, these texts also contain a wealth of knowledge and observations about the natural world. Modern scientific discoveries have confirmed many of these observations, suggesting that ancient Indian societies were more advanced scientifically than commonly thought.
The Vedas, for example, contain detailed descriptions of the universe, including its origin, structure, and functioning. They describe the sun, moon, stars, and planets and their orbits, as well as the cycles of day and night, seasons, and eclipses. The Puranas contain descriptions of various living creatures, including humans, animals, and plants, and their characteristics, behavior, and habitat.
Recent scientific discoveries have confirmed many of these ancient observations. For example, the Vedic description of the universe as a cyclical process of creation and destruction is consistent with modern cosmological theories, such as the Big Bang and the cyclic universe model. The Vedas also describe the concept of relativity and the unity of matter and energy, which are fundamental principles of modern physics.
Similarly, the Puranas contain detailed descriptions of the human body, including its anatomy, physiology, and pathology. Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, is based on these observations and provides a comprehensive understanding of health and disease. Modern research has confirmed the efficacy of Ayurvedic treatments and has led to the discovery of new therapeutic compounds.
It is clear that ancient Indian societies had a deep understanding of the natural world and made significant contributions to scientific knowledge. However, it is important to note that scientific progress is not linear and is influenced by various social, political, and economic factors. While ancient Indian societies may have been more advanced scientifically in certain areas, they also faced limitations and challenges that impeded progress in other areas.
Furthermore, modern scientific discoveries have expanded our understanding of the natural world and have enabled us to develop new technologies and improve our quality of life. While we can learn from the insights of ancient Indian scriptures, we must also recognize the value of modern scientific methods and knowledge.
In conclusion, ancient Indian scriptures contain a wealth of knowledge and observations about the natural world that have been confirmed by modern scientific discoveries. While ancient Indian societies were more advanced scientifically in certain areas, they also faced limitations and challenges. We must appreciate the insights of ancient Indian scriptures while also recognizing the value of modern scientific knowledge and methods.
It would be incorrect to conclude that modern science is merely rediscovering what was already known in ancient India. While ancient Indians certainly made significant scientific discoveries and observations, modern science has advanced considerably in terms of technology, methodology, and knowledge. Modern science has built upon the foundation laid by ancient Indian scholars and has made many discoveries and breakthroughs that were not possible in ancient times.
It is important to recognize that scientific progress is a continuous and cumulative process. Each generation builds upon the knowledge and discoveries of the previous generation, and discoveries are made as a result of advancements in technology, methodology, and understanding. While ancient Indians made important contributions to science, modern science has made significant progress in many areas, such as medicine, physics, chemistry, and engineering.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that scientific knowledge is not static, but constantly evolving. Discoveries are made all the time, and scientific theories and models are refined and revised as new evidence emerges. Therefore, it would be inaccurate to suggest that modern science is merely rediscovering what was already known in ancient India.
There are several possible explanations for how ancient Indians could have known about the scientific facts mentioned in their scriptures. Some scholars believe that ancient Indian scientists and scholars may have made these discoveries through careful observation and experimentation, using methods that were passed down through generations.
Others argue that ancient Indian knowledge was based on a deep understanding of spiritual and philosophical concepts, which allowed scholars to make intuitive leaps and connections between seemingly unrelated fields of study. For example, some scholars believe that the concept of "prana" (life force energy) in Ayurvedic medicine may be linked to the modern concept of energy in physics.
Still, others believe that ancient Indian knowledge may have been passed down from more advanced civilizations that existed in ancient times. For example, some scholars believe that the ancient Indus Valley civilization may have had advanced knowledge of metallurgy and urban planning that was later passed down to the Vedic civilization.
Ultimately, the origins of ancient Indian knowledge remain the subject of ongoing research and debate. What is clear, however, is that the scientific and intellectual legacy of ancient India is vast and continues to inspire and inform scientific research today.
While ancient Indians made significant scientific discoveries and observations, modern science has advanced considerably in terms of technology, methodology, and knowledge. Modern science has built upon the foundation laid by ancient Indian scholars and has made many discoveries and breakthroughs that were not possible in ancient times. Therefore, it would be incorrect to conclude that modern science is simply rediscovering what was already known in ancient India.
There are several scientific facts mentioned in ancient Indian scriptures that have been verified by modern science. Here are some examples:
- The concept of atoms: The ancient Indian text, the Vaisheshika Sutra, describes atoms as the smallest indivisible units of matter. Modern science has confirmed the existence of atoms and their role as the building blocks of matter.
- The Earth’s rotation: The Rigveda describes the Earth as rotating on its axis, which was later confirmed by modern science.
- The heliocentric model of the solar system: The Surya Siddhanta, an ancient Indian text, describes the sun as the center of the solar system with the planets orbiting around it. This is consistent with the modern heliocentric model of the solar system.
- Ayurveda: Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine, describes the importance of a healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle in maintaining good health. Modern science has confirmed the importance of these factors in preventing disease and promoting overall health.
- Yoga: The ancient Indian practice of yoga has been found to have numerous health benefits, including reducing stress, improving flexibility, and enhancing mental clarity. Modern research has confirmed the efficacy of yoga in promoting physical and mental well-being.
- The water cycle: The ancient Indian text, the Vishnu Purana, describes the water cycle, including the evaporation of water from the oceans and its precipitation as rain. This is consistent with modern scientific understanding of the water cycle.
- Plastic surgery: The ancient Indian text, the Sushruta Samhita, describes various surgical procedures, including rhinoplasty (nose surgery) and reconstructive surgery. These techniques are effective and are still used today.
- Astronomy: The ancient Indian text, the Siddhanta Shiromani, contains detailed astronomical observations and calculations, including the distance between the earth and the moon, the size and shape of the earth, and the duration of the day and night. Modern science has confirmed many of these calculations.
- Mathematics: Ancient Indian mathematicians made significant contributions to the field, including the invention of the decimal system and the concept of zero. These concepts were later adopted by the Arab world and Europe, leading to the development of modern mathematics.
- Sound and music: The ancient Indian text, the Natyashastra, describes the physics of sound and the science of music, including the relationship between musical notes and mathematical ratios. Modern science has confirmed the relationship between sound and mathematics and the importance of music in promoting physical and emotional well-being.
- Botany: The ancient Indian text, the Charaka Samhita, describes the properties and uses of various plants and herbs in medicine. Many of these plants have been found to have medicinal properties and are still used in modern medicine.
- Metallurgy: The ancient Indian text, the Arthashastra, contains detailed descriptions of metallurgy, including the extraction and purification of metals such as gold and silver. Modern science has confirmed the accuracy of these descriptions and techniques.
- Architecture and urban planning: The ancient Indian text, the Manasara, contains detailed instructions on the design and construction of buildings and cities, including the use of geometry and mathematics in architecture. Many ancient Indian cities were designed according to these principles, and some of them still exist today.
- Environmental conservation: The ancient Indian text, the Manusmriti, contains guidelines for environmental conservation, including the protection of forests and wildlife. These ideas are still relevant today and have been incorporated into modern environmental conservation efforts.
- Genetics: The ancient Indian text, the Mahabharata, contains references to genetic traits and heredity, including the passing on of physical and behavioral characteristics from parents to offspring. This is consistent with the modern understanding of genetics.
- Psychology: The ancient Indian text, the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, describes the workings of the human mind and the techniques for achieving mental balance and clarity. Many of these techniques, such as meditation and mindfulness, have been found to have therapeutic benefits and are widely used in modern psychology.
- Geology: The ancient Indian text, the Brihat Samhita, contains descriptions of various geological features, such as mountains, rivers, and earthquakes. These descriptions are consistent with modern scientific understanding of geology.
- Agriculture: The ancient Indian text, the Arthashastra, contains detailed instructions on agriculture, including irrigation techniques, crop rotation, and soil conservation. Many of these techniques are still used today and be effective in improving crop yields and soil health.
- Medicine: The ancient Indian texts, the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita describe various medical conditions and their treatments, including surgical procedures such as cataract surgery and rhinoplasty. Many of these techniques are still used in modern medicine.
- Astronomy and astrology: Ancient Indian texts, such as the Brihat Jataka and the Surya Siddhanta, contain detailed observations of the movement of celestial bodies and their influence on human affairs. While modern science has debunked the idea of astrology, the accurate astronomical observations and calculations made by ancient Indian scholars have been validated by modern scientific research.
- Physics: The ancient Indian text, the Surya Siddhanta, contains detailed observations of the physical properties of the sun, including its size, temperature, and gravitational pull. These observations were made centuries before similar discoveries were made in the West.
- Philosophy: Ancient Indian philosophical texts, such as the Vedas and Upanishads, contain profound insights into the nature of reality and consciousness. These ideas have influenced modern philosophy and have been the subject of ongoing scientific research in fields such as neuroscience and psychology.
- Linguistics: The ancient Indian text, Panini's Ashtadhyayi, contains a detailed analysis of the structure of Sanskrit grammar. This analysis is consistent with modern linguistic theories and has influenced the development of linguistic research.
- Mathematics: Ancient Indian mathematicians made significant contributions to the development of mathematics, including the invention of the decimal system and the concept of zero. These ideas were not widely adopted in the West until several centuries later.
- Metallurgy: The ancient Indian text, the Arthashastra, contains detailed instructions on metallurgy, including the extraction and purification of metals such as gold, silver, and copper. These techniques were highly advanced for their time and have been the subject of ongoing research in modern metallurgy.
- Ayurveda: Ayurveda is an ancient Indian system of medicine that focuses on maintaining balance and harmony within the body. It emphasizes the use of natural remedies and lifestyle changes to prevent and treat illness. While some aspects of Ayurveda are effective, others remain controversial and are the subject of ongoing research.
- Music: Ancient Indian texts, such as the Natyashastra, contain detailed descriptions of music theory and practice, including the use of different scales and rhythms. Many of these ideas have influenced modern music theory and continue to inspire contemporary musicians.
- Ethics: Ancient Indian texts, such as the Bhagavad Gita, contain profound insights into ethical behavior and the nature of the self. These ideas have influenced modern philosophy and have been the subject of ongoing research in fields such as psychology and neuroscience.
- Sociology: Ancient Indian texts, such as the Arthashastra, contain detailed observations and insights into social structures and human behavior. These ideas have influenced modern sociology and continue to inform ongoing research in the field.
The advanced scientific knowledge that existed in ancient India is evidenced by the numerous scientific facts mentioned in their scriptures that have been confirmed by modern science. These examples demonstrate the breadth and depth of scientific knowledge that existed in ancient India and the significant contributions made by ancient Indian scholars to various fields of science. While modern science has made many discoveries and advancements, it is important to acknowledge and appreciate the scientific legacy of ancient India and how it has informed and inspired modern scientific research. However, it is important to note that ancient Indian knowledge was not always scientifically accurate or applicable to all fields, and some ideas remain controversial and the subject of ongoing research and debate. Nevertheless, the contributions made by ancient Indian scholars to the development of science and knowledge cannot be denied and continue to influence modern science and research today.
There is no direct mention of computers in ancient Indian scriptures, as the concept of modern-day computers did not exist during that time. However, there are some references to devices and machines that have been interpreted by some scholars as possible references to advanced technological devices, including computers.
For example, the ancient Indian epic, the Mahabharata, mentions a flying machine called the Vimana, which was said to be powered by a mysterious energy source called the "Meru-ghanta." Some scholars have interpreted this Vimana as a type of advanced aircraft or even a spacecraft. Similarly, the ancient Indian text, the Sushruta Samhita, mentions a device called the Yantra Sarvasva, which is believed by some to be a type of advanced surgical instrument that may have had some computing capabilities.
It is important to note, however, that these interpretations are highly speculative and are not supported by any concrete evidence or scientific proof. While ancient Indian scholars may have had advanced knowledge of mathematics, astronomy, and other fields, the concept of modern-day computers, as we know them today, did not exist during that time.
Therefore, while there may be some references in ancient Indian scriptures that suggest advanced technological devices, it is important to approach these interpretations with caution and not assume that they refer to modern-day computers or other advanced devices.
There are references to aircraft-like devices in ancient Indian scriptures. The most famous of these references are found in the ancient Indian epic, the Ramayana, which describes a flying chariot called the Pushpaka Vimana. According to the text, the Pushpaka Vimana was a large, beautiful, and highly advanced flying vehicle that could travel great distances in the air. It was described as being powered by a "powerful aerial motor" and was said to be able to fly at incredible speeds.
Similarly, the Mahabharata, another ancient Indian epic, also contains references to flying machines called Vimanas. These Vimanas were described as being able to fly great distances and even travel to other planets. The text also mentions the use of various weapons and defenses on these Vimanas, suggesting that they were highly advanced and sophisticated machines.
Some scholars have suggested that these references to flying machines may be symbolic or metaphorical, rather than literal descriptions of actual aircraft. Others, however, have suggested that these descriptions may be evidence of advanced technological knowledge in ancient India, and may even indicate the existence of some type of flying device during that time.
It is important to note that there is no concrete evidence to support the existence of actual flying machines in ancient India, and much of the evidence for these devices comes from interpretations of ancient texts. Nevertheless, these references to aircraft-like devices in ancient Indian scriptures are intriguing and suggest that ancient Indian scholars had a keen interest in the possibilities of flight and advanced technology.
The History and Meaning Behind the LEGO Brand

The word "LEGO" is indeed derived from the Danish phrase "Leg Godt," which means "play well" in English. LEGO was founded in Denmark in 1932 by Ole Kirk Christiansen, who started by making wooden toys before transitioning to plastic bricks in the late 1940s. The LEGO Group trademarked the name "LEGO" in 1934, and the company has been using the name ever since.
It's interesting to note that in Latin, the word "LEGO" means "I put together" or "I assemble." This Latin meaning is particularly relevant to the LEGO brand because it emphasizes the importance of the building aspect of the toy. LEGO sets are designed to encourage creativity and problem-solving, as children construct models using the interlocking bricks.
The name "LEGO" perfectly captures the essence of the toy. It emphasizes the importance of play and creativity while also highlighting the fundamental building aspect that makes LEGO sets so unique and engaging.
The history of LEGO dates back to 1932 when a Danish carpenter named Ole Kirk Christiansen started a small company in Billund, Denmark, making wooden toys.
After World War II, LEGO began producing plastic toys, and in 1949, they introduced the LEGO brick, which would become their flagship product. The interlocking plastic bricks allowed children to build and create different structures, sparking their imagination and creativity. Over the years, LEGO has expanded its product line to include themed sets, such as space exploration, castle building, and even popular franchises like Star Wars and Harry Potter.
In the 1960s and 70s, LEGO faced financial difficulties due to the rise of electronic toys, but they were able to recover by diversifying their product line and expanding their global presence. Today, LEGO is one of the most recognizable toy brands in the world, with a presence in more than 140 countries and a product line that includes not only traditional bricks but also video games, theme parks, and movies.
LEGO's enduring popularity can be attributed to its ability to evolve with the times while still staying true to its core principles of encouraging creativity, imagination, and problem-solving through play.
The Digital Immune System: Importance, Implementation, Best Practices, and Risks

As organizations increasingly rely on digital technology to conduct their operations, the need for a Digital Immune System has become more critical. This article will explore what a Digital Immune System is, why it is important, how it can be implemented, best practices for maintaining it, as well as the advantages and risks associated with its use.
In today's world, where digitalization has become the norm, the concept of a "Digital Immune System" has gained immense importance. A Digital Immune System refers to a set of technologies, tools, and practices that are employed to detect, prevent, and respond to digital threats such as cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other security vulnerabilities.
The Importance of Digital Immune System: In the digital era, where most businesses operate online, the protection of digital assets has become critical. Cybersecurity threats have become increasingly sophisticated, and the damage they cause can be catastrophic. Therefore, a Digital Immune System is crucial to protect digital assets from potential threats and attacks. It can help businesses detect and prevent unauthorized access to their networks, protect sensitive data, and mitigate the impact of a security breach.
Implementation Method: The implementation of a Digital Immune System involves several steps, including risk assessment, technology deployment, training of employees, and ongoing monitoring and updating. The first step in implementing a Digital Immune System is to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats by conducting a risk assessment. This helps organizations understand the risks they face and prioritize their security measures.
Next, organizations must deploy appropriate technology to protect their digital assets. This can include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption tools, and antivirus software. However, it is not enough to rely solely on technology. Employees must be trained on best practices, such as using strong passwords, identifying phishing emails, and avoiding suspicious websites.
Finally, organizations must continuously monitor and update their Digital Immune System to ensure it remains effective against evolving threats.
Best Practices: To ensure the effectiveness of a Digital Immune System, organizations should follow certain best practices. These include:
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and threats
- Deploying a combination of technology tools and practices
- Implementing strict access controls to limit unauthorized access
- Training employees on cybersecurity best practices
- Regularly monitoring and updating the system to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Advantages: A Digital Immune System offers several advantages to businesses. These include:
- Protection of digital assets from cyber threats
- Early detection and prevention of security breaches
- Mitigation of the impact of security breaches
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Increased customer trust and confidence.
Risks: While a Digital Immune System provides significant benefits, there are also risks associated with its implementation. These include:
- High costs associated with deploying and maintaining the system
- The potential for false alarms, which can create a sense of complacency among employees
- The risk of over-reliance on technology, leading to the neglect of training and awareness programs
- The potential for human error, such as employees failing to follow best practices or falling for phishing scams.
A Digital Immune System is a crucial tool for businesses operating in the digital age. It helps protect digital assets from cyber threats, provides early detection and prevention of security breaches, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. However, organizations must follow best practices to ensure the effectiveness of their Digital Immune System while also mitigating the associated risks.
There are many products available that can help organizations implement a Digital Immune System.
Here are a few examples of commonly used products, along with their advantages and disadvantages:
- Firewall: A firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a set of predefined rules. Advantages of a firewall include:
- Protects against unauthorized access to the network
- Helps prevent malware infections
- Can be configured to block specific types of traffic
- Provides a single point of control for network security
Disadvantages of a firewall include:
- Can create a false sense of security if not properly configured
- May not be effective against advanced threats such as zero-day attacks
- Can affect network performance if not properly optimized
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): An IDS is a software or hardware system that monitors network traffic for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activity. Advantages of an IDS include:
- Provides early warning of potential security breaches
- Can detect both known and unknown threats
- Can be configured to trigger automated responses to threats
Disadvantages of an IDS include:
- Requires constant monitoring to be effective
- Can generate false alarms, leading to security fatigue among employees
- May not be effective against sophisticated attacks that are designed to evade detection
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software is a type of software designed to detect and remove malware from a computer system. Advantages of antivirus software include:
- Provides real-time protection against malware infections
- Can scan both incoming and outgoing email attachments
- Can detect and remove known threats
Disadvantages of antivirus software include:
- May not be effective against advanced threats such as zero-day attacks
- Requires constant updates to stay effective
- Can affect system performance if not properly optimized
- Encryption Tools: Encryption tools are used to protect data by converting it into a code that can only be deciphered with a specific key. Advantages of encryption tools include:
- Protects data from unauthorized access
- Helps maintain the confidentiality of sensitive data
- Can be used to meet regulatory compliance requirements
Disadvantages of encryption tools include:
- Can affect system performance if not properly optimized
- Can be difficult to implement and manage
- Requires constant updates to stay effective
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA is a security process in which a user provides two forms of authentication to verify their identity. This can include something they know, such as a password, and something they have, such as a mobile device. Advantages of 2FA include:
- Provides an additional layer of security beyond passwords
- Helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data
- Can be used to meet regulatory compliance requirements
Disadvantages of 2FA include:
- Can be time-consuming and inconvenient for users
- May not be effective against sophisticated attacks that are designed to bypass 2FA
- Can be difficult to implement and manage for large organizations.
In conclusion, there are many products available that can help organizations implement a Digital Immune System. Each product has its advantages and disadvantages, and organizations must carefully evaluate their needs and requirements before selecting the products that will best meet their needs.
The Power of FOCUS: Follow One Course Until Successful

In a world filled with distractions and competing priorities, it can be challenging to stay focused on achieving our goals. However, adopting a FOCUS mindset can be a game-changer when it comes to achieving success. In this article, we'll explore the power of FOCUS and how it can help you achieve your goals.
FOCUS is an acronym for "Follow One Course Until Successful" and is a popular phrase that emphasizes the importance of staying committed to a single goal or objective until it is achieved.
There are several benefits to adopting a FOCUS mentality. Firstly, it allows you to direct all your energy and efforts towards a specific outcome, increasing the chances of achieving success. Secondly, it helps to avoid distraction and reduce the likelihood of becoming overwhelmed or scattered. Finally, focusing on a single goal can help you develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter or task at hand.
However, it's important to note that FOCUS does not necessarily mean ignoring everything else in your life. It's still important to maintain a balance and prioritize self-care and other responsibilities. Additionally, there may be situations where pivoting or adjusting your approach is necessary, even if it means temporarily shifting focus away from your original goal.
FOCUS can be a useful mindset to adopt when working towards a specific objective, but it's important to maintain flexibility and balance in other areas of your life.