Cataloguing Strategic Innovations and Publications
Impact of Information Technology on the Construction Industry
Information Technology (IT) and computers play a crucial role in the construction industry. IT helps streamline processes, improve project management, and enhance collaboration between team members. The impact of IT has been significant, with increased productivity, efficiency, and cost savings being some of the key benefits.
Products designed specifically for construction include Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, project management tools, and collaboration platforms. BIM software provides a digital representation of the building design and construction process, allowing for better visualization and collaboration between design and construction teams. Project management tools help manage schedules, budgets, and resources, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns. Collaboration platforms allow for real-time communication and collaboration between team members, regardless of location.
Advantages of using IT and computer products in the construction industry include improved accuracy and quality, reduced rework, better project visualization, and increased collaboration.
Disadvantages include a steep learning curve for new users, potential resistance to change among some team members, and a dependence on technology, which can lead to increased risk if there are problems with the technology.
Information Technology (IT) is used in various stages of the building planning, design, and construction process to streamline processes, improve project management, and enhance collaboration. Some ways IT is used in the building industry include:
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM) - BIM software is used to create digital models of the building, including architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems. BIM allows for better visualization and collaboration between design and construction teams and improved accuracy and quality in the design process.
2. Project Management - IT tools are used to manage schedules, budgets, and resources, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns. Project management tools allow for real-time monitoring and tracking of project progress, making it easier to identify and resolve issues.
3. Collaboration - Collaboration platforms allow team members to communicate and share information in real time, regardless of location. This enhances collaboration between team members and improves project efficiency.
4. Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality - Virtual and augmented reality technologies allow for immersive visualization of the building design and better communication and decision-making between team members.
5. Drones - Drones equipped with cameras and sensors are used for aerial surveying, allowing for more accurate mapping of the site. Drones can also be used for construction site inspections, reducing the need for manual inspections and improving safety.
Some of the popular BIM (Building Information Modeling) products in the market include:
Autodesk Revit - Offers comprehensive BIM tools for architecture, engineering, and construction.
o Advantages: Robust feature set, strong integration with other Autodesk products, widely used in the industry.
o Disadvantages: Steep learning curve, high cost of ownership.
Bentley MicroStation - Provides BIM tools for architecture, engineering, and construction, as well as for geospatial information.
o Advantages: Wide range of features, flexible modeling options, and good support for large projects.
o Disadvantages: Steep learning curve, limited integration with other software.
ArchiCAD - BIM software designed specifically for architects.
o Advantages: User-friendly interface, strong focus on architectural design, integration with other tools.
o Disadvantages: Limited support for engineering and construction, the higher cost compared to some other BIM products.
SketchUp - Simple BIM software designed for architecture, engineering, and construction.
o Advantages: Intuitive user interface, low cost of ownership, strong community support.
o Disadvantages: Limited feature set compared to other BIM products, limited support for large projects.
These are just a few examples of the BIM products available in the market. Each product has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice for a specific project will depend on the needs and requirements of the project team.
Information Technology (IT) can be used for material handling and cost savings in building construction in several ways, including:
- Inventory Management - IT tools can be used to manage the inventory of building materials, tracking quantities, location, and delivery schedules. This helps ensure that materials are available when needed, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
- Logistics and Delivery Management - IT tools can be used to optimize delivery routes and schedules, reducing transportation costs and minimizing the time required for material deliveries to the construction site.
- Waste Management - IT tools can be used to track and monitor waste on construction sites, reducing the amount of waste generated and improving cost savings.
- Supply Chain Management - IT tools can be used to manage the supply chain of building materials, improving the procurement process and reducing costs. This includes managing contracts, procurement processes, and communication with suppliers.
- Real-Time Monitoring - IT tools can be used to monitor construction sites in real time, providing information on material usage and waste generation. This helps teams make informed decisions, reducing waste and improving cost savings.
Information Technology (IT) can also be used to improve building strength and structural integrity in several ways, including:
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM) - BIM software can be used to create detailed digital models of building structures, including architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems. This helps identify potential structural weaknesses and enables teams to make informed decisions about the design and construction process, improving the building's strength and integrity.
2. Structural Analysis - IT tools can be used to perform advanced structural analysis, including finite element analysis and linear/non-linear analysis. This helps teams design safer and stronger structures, improving the building's stability and reducing the risk of failure.
3. Real-Time Monitoring - IT tools can be used to monitor structures in real time, providing information on any changes in the building's behavior. This can help teams identify potential issues early and make informed decisions to improve the building's strength and integrity.
4. Simulation and Testing - IT tools can be used to simulate various scenarios and test building structures, allowing teams to identify potential issues and make informed decisions about the design and construction process.
5. Quality Control - IT tools can be used to automate quality control processes, ensuring that materials and construction practices meet established standards. This helps improve the building's strength and integrity, reducing the risk of failure.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems also help the construction industry in several ways, including:
1. Project Management - ERP systems can help manage all aspects of the construction project, including schedules, budgets, and resources. This helps improve project planning and tracking, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns.
2. Financial Management - ERP systems can integrate all financial processes, including accounting, payroll, and procurement. This helps improve the accuracy of financial information and enables teams to make informed decisions about project finances.
3. Supply Chain Management - ERP systems can help manage the procurement of materials, suppliers, and contracts. This helps improve the efficiency of the procurement process and reduces the risk of material shortages.
4. Human Resources Management - ERP systems can help manage human resources processes, including payroll, time and attendance, and employee benefits. This helps improve the efficiency of HR processes and reduces administrative burdens.
5. Quality Control - ERP systems can help manage quality control processes, ensuring that materials and construction practices meet established standards. This helps improve the quality of construction projects and reduces the risk of failure.
6. Reporting and Analytics - ERP systems can provide real-time data and analytics, helping teams make informed decisions about the project. This includes data on project progress, resource utilization, and financial performance.
There are several Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) products available for the construction industry, including:
Procore - Procore is a cloud-based construction management software that provides project management, financial management, and supply chain management solutions for the construction industry.
Advantages of Procore include its user-friendly interface, real-time project data, and mobile app.
Disadvantages include its limited customization options and high cost.
PlanGrid - PlanGrid is a construction collaboration platform that provides project management, field management, and communication solutions for the construction industry.
Advantages of PlanGrid include its real-time collaboration features and integration with BIM software.
Disadvantages include its limited financial management features and high cost.
Oracle Primavera P6 - Oracle Primavera P6 is a project management software that provides project scheduling, resource management, and project control solutions for the construction industry.
The advantages of Primavera P6 include its advanced project scheduling features and integration with other Oracle products.
Disadvantages include its complex user interface and high cost.
Aconex - Aconex is a cloud-based construction management software that provides project management, document management, and collaboration solutions for the construction industry.
Advantages of Aconex include its robust document management features and integration with BIM software.
Disadvantages include its limited customization options and high cost.
CMiC - CMiC is an enterprise resource planning software that provides project management, financial management, and supply chain management solutions for the construction industry.
The advantages of CMiC include its robust financial management features and integration with other CMiC products.
Disadvantages include its limited customization options and high cost.
There are several ERP products available for the construction industry, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The choice of ERP software will depend on the specific needs of the construction company and the features that are most important to their business.
1. The role of IT and computers in the construction industry continues to grow, and the impact has been positive over the past decade. While there are some potential disadvantages, the advantages of using IT and computer products outweigh them and the construction industry continues to adopt and embrace technology.
2. IT is widely used in the building planning, design, and construction industry to improve processes, enhance collaboration, and increase efficiency. The use of IT continues to grow in the industry, and the impact has been significant in the past decade.
3. IT can play a crucial role in improving building strength and structural integrity. The use of IT tools can help teams make informed decisions about the design and construction process, reducing the risk of failure and improving the overall quality of the building.
4. ERP systems can play a crucial role in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of construction projects. The use of ERP systems can help streamline processes, improve project management, and enhance collaboration, resulting in improved project outcomes and cost savings.
5. IT can play a crucial role in improving material handling and reducing costs in building construction. The use of IT tools can help streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance collaboration, resulting in improved project outcomes and cost savings.
Project Management Office

Implementing a Project Management Office (PMO):
4 Steps to Success
While every project is different, a standardized set of processes and practices can simplify the management of multiple projects and maximize the chances for success. Many businesses use a project management office (PMO) to provide this consistency: 89% of organizations have at least one PMO, a recent report found. Today’s PMO acts as a center of excellence, providing expertise, support, and guidance across an organization.
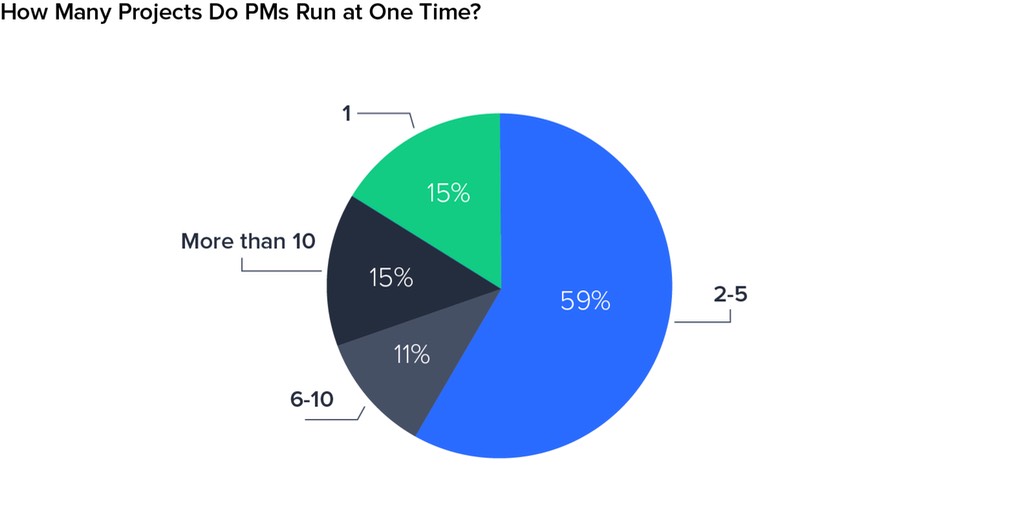
Project environments are dynamic, and PMOs help organizations gain alignment across multiple project teams, with greater governance and better risk management. With 59% of project managers now running two to five projects simultaneously, and 11% taking on six to 10 at one time, a PMO has become a critical support function. Many successful PMOs work with the C-suite to gain executive buy-in and ensure that the project portfolio is aligned with organizational strategy.
More and more companies are recognizing the value a PMO can offer, but establishing one is a complicated undertaking, with many challenges to overcome and choices to make. During my two decades in project management, I have consulted for numerous PMOs and have gained insight into the skills needed to lead one and the best ways to approach implementation.
What Value Does a PMO Bring?
Any PMO is only as good as its leadership and implementation. When functioning optimally, a PMO will:
- Define, standardize, and maintain best practices and processes across departments.
- Enhance compliance and governance.
- Offer direction and guidance to project managers.
- Manage and allocate resources across projects based on schedules, priorities, and budgets.
- Provide accurate, up-to-date financial and status reports to management and executive leadership.
- Define project selection criteria and align the organizational portfolio with business goals and strategy.
- Improve stakeholder collaboration and satisfaction by setting rules for project culture and cross-departmental communication, as well as consistent training on methodologies, techniques, and best practices.
PMO vs. PM: What’s the Difference?
Although the PMO deals with project management, the two functions operate very differently. Here is a high-level view of how they work together: A PMO leader should:
- Have a solid understanding of project management methodologies and tools.
- Be a visionary with exceptional communication, interpersonal, and strategic skills.
- Have experience with organizational change and know what is needed to make that happen.
- Be up to date with the latest trends in project management.
A common mistake executives make is to hand control of the PMO to their lead project manager. This person may be good at managing projects, but the expertise they apply in day-to-day project management may not meet the required depth of knowledge around standards, processes, or management.
4 Essential Steps to Establishing a PMO
Just as with any project, when setting up a PMO, you need to assess, analyze, and plan. Follow these four steps for a successful implementation:
1. Assess the Current State
Before you start, you must consider the type of PMO you want. Think about what exactly it is that you want to achieve: What should the future state of project management in the organization look like? This will help you highlight the gaps and identify which areas the PMO will aim to address.
There are several types of PMO, and which one you choose will vary according to business needs and the project management maturity within the company (more mature organizations may require less oversight). PMOs are categorized by the level of control they exercise:
- Supportive: A supportive PMO has a low degree of control. It supports all projects by providing training, templates, and best practices. It operates as a consultant or advisor.
- Controlling: A controlling PMO checks if the project management tools, standards, and processes are being applied to projects. It doubles as an auditor and an advisor.
- Directive: A directive PMO maintains a high degree of control and is responsible for the execution of projects. Project managers report to the PMO.
2. Create a Roadmap and Define KPIs
A PMO is made up of three interdependent components: functional, structural, and disciplinary. Define how each component will operate to ensure there is no uncertainty around its responsibilities, goals, or place in the context of the wider business.
Functional Component
Understanding the scope and purpose of the PMO is an important step in determining how it will function. This component could be:
- Setting standards: Establishing processes, templates, and systems, as well as training and coaching project managers.
- Portfolio management: Select projects that are aligned with the overall organizational strategy.
- Governance: Auditing and reviewing project management processes and ensuring project managers are adhering to them.
- Project delivery: Identifying risks and monitoring progress.
Structural Component
You will also need to define the people, processes, and tools that make up your PMO:
- People: The PMO team must be strategic thinkers well versed in project management methodologies and tools who are comfortable communicating with higher management.
- Processes: These will be based on the PMO’s disciplinary components (see below). Processes should be practical, adaptable, and scalable.
- Tools: These encompass all the ways knowledge will be disseminated by the PMO, ranging from simple templates to sophisticated project management systems.
Disciplinary Component
Your PMO may be managing:
- Resources such as people, equipment, tools, vendors, contracts, and other assets.
- Communication between project managers and stakeholders, particularly project information and status reports.
- Projects to ensure key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics are within acceptable ranges and making adjustments to improve.
- Risk by identifying and highlighting any possible risks, particularly those resulting from change management.
Now that you have defined the components and areas of intervention, you can work with stakeholders to prioritize requirements and create a step-by-step roadmap that lays out a PMO strategy for setup and optimization.
Next, identify the KPIs that will be used to measure PMO performance and how you will gather timely, accurate data. KPIs can be built around task completion or milestones, realized benefits of delivered projects and programs, strategic alignment across the portfolio, resource utilization, and more, but you should aim to have KPIs for each of these main areas:
- Practices, methodologies, and tools
- Solution delivery and execution
- Monitoring and control
- People and capabilities
3. Implement the PMO
Organizational change can be difficult, and it’s important to be patient while mindsets shift. You should identify the most problematic processes and prioritize fixing these first, automate tedious tasks where possible, and set up notifications and reminders for deadlines. How project managers respond to the introduction of a PMO will be a decisive factor in its success. Achieving small wins quickly can help to grow their buy-in, as they start to see the value a PMO can offer. Be sure to recognize the efforts of project managers, fulfill their needs where possible, and provide full support and training.
If your organization is large, you can use pilot teams to gain feedback on changes before the organization-wide rollout—this will allow you to make improvements and remedy any initial problems.
4. Review Regularly and Make Improvements
A PMO is not a stagnant entity—it will evolve with the growth of project managers’ skills and knowledge and with enhancements to systems and tools. Regularly review data to monitor performance drive improvements, and update your KPIs over time as the PMO matures. The PMO must stay aligned with the organization; when business strategy shifts, the PMO strategy must shift along with it.
Ultimately, every organization is different and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to PMO implementation. It demands diligence and care. Try not to deviate from your goals, keep the overall objectives in mind, regularly communicate progress to stakeholders, and address any concerns promptly.
A Catalyst for Greater Efficiency
A well-executed PMO offers many benefits but demands a huge amount of effort and change to establish. While a PMO is often viewed as an administrative function, gaining buy-in is central to its effectiveness and should not be an afterthought. A PMO should be a catalyst for greater accountability, synergy, and discipline, and above all should foster greater efficiency, enabling project managers to do more with less.
Root cause analysis (RCA)
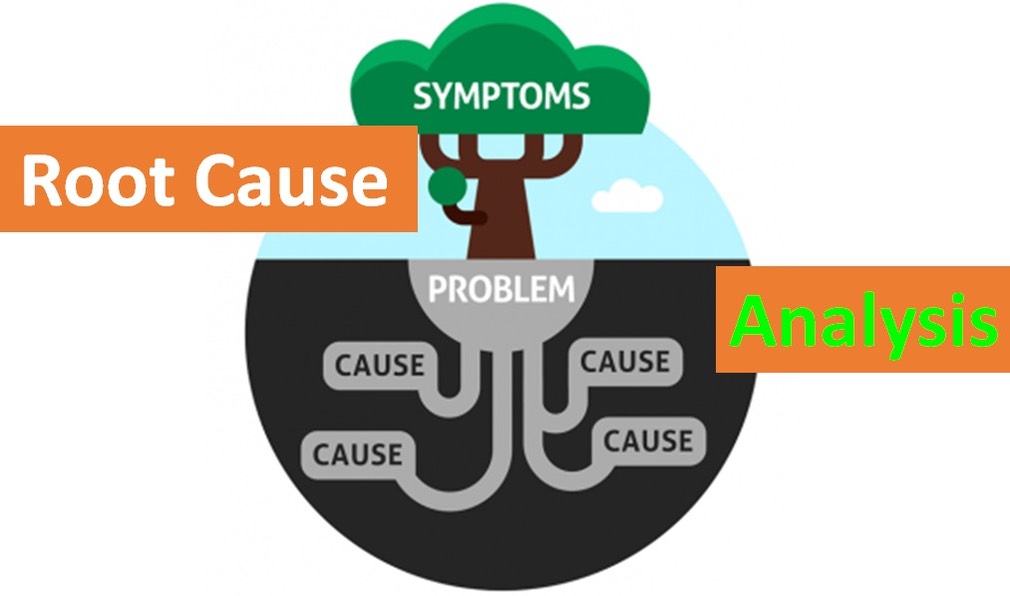
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem or incident. RCA aims to identify the root cause so that effective corrective action can be taken to prevent the problem from recurring. There are several different methodologies used in RCA, including the 5 Whys, Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram, and Fault Tree Analysis.
The advantages of RCA include:
- Identifying the underlying cause of a problem, rather than just treating the symptoms
- Improving the efficiency and effectiveness of corrective actions
- Reducing the likelihood of the problem recurring
The disadvantages of RCA include:
- It can be time-consuming and resource-intensive
- It can be difficult to identify the true root cause of a problem
- It may not be effective if the wrong methodology is used or if it is not implemented correctly.
To implement RCA correctly, it is important to:
- Select the appropriate methodology for the problem or incident being investigated
- Gather and analyze data related to the problem or incident
- Identify the root cause of the problem or incident
- Develop and implement effective corrective action to prevent the problem from recurring
- Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the corrective action.
Methodologies used in RCA,
- The 5 Whys is a simple problem-solving technique that involves asking "why" a problem occurred and then asking "why" to each answer until the root cause of the problem is identified. The name "5 Whys" comes from the idea that it usually takes five iterations of asking "why" to get to the root cause.
- Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram, also known as a cause-and-effect diagram or Ishikawa diagram, is a visual tool used to identify all of the possible causes of a problem or effect. It is often used in manufacturing and service industries to identify the root causes of quality control issues. The diagram is shaped like a fishbone, with the problem or effect written at the head and the various causes branching out from the spine.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a method used to identify the causes of an event or incident. It is often used in safety-critical industries such as aviation, nuclear power, and chemical manufacturing to identify the chain of events that led to an accident. A fault tree is a graphical representation of the logic of the events leading to an accident. It is organized in a top-down tree structure, with the event of interest as the root node, and the contributing factors as the branches of the tree. The leaf nodes represent the basic events that contribute to the accident.
These three methodologies are commonly used in Root Cause Analysis, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The 5 Whys is simple and easy to use, but it may not be the best choice for complex problems. Fishbone diagrams are great for visualizing the relationships between different factors and causes. Fault Tree Analysis is great for identifying the chain of events leading to an incident, but it can be time-consuming and complex to construct. The best methodology to use will depend on the problem or incident being investigated, and the resources available.
RCA is useful in information technology (IT) for identifying the underlying causes of problems or incidents, such as software bugs, system failures, and security breaches. By identifying the root cause of a problem, IT teams can take effective corrective action to prevent the problem from recurring. This can help improve the overall performance and reliability of IT systems, as well as reduce the risk of data loss or security breaches.
Here are a few examples of how RCA is used in IT:
- Software bugs: When a software bug is reported, an RCA can be conducted to identify the root cause of the problem. This could involve analyzing log files, reviewing code, or conducting user interviews to determine the conditions that led to the bug. Once the root cause is identified, appropriate corrective action can be taken to fix the bug and prevent it from happening again in the future.
- System failures: When a system failure occurs, an RCA can be conducted to identify the cause of the failure. This could involve analyzing system logs, reviewing system configurations, or conducting interviews with system administrators. Once the root cause is identified, appropriate corrective action can be taken to prevent the failure from happening again in the future.
- Security breaches: When a security breach occurs, an RCA can be conducted to identify the cause of the breach. This could involve analyzing network logs, reviewing security configurations, or conducting interviews with system administrators. Once the root cause is identified, appropriate corrective action can be taken to prevent the breach from happening again in the future.
Overall, RCA is a valuable tool for IT teams to quickly identify and fix problems and improve the overall performance, reliability, and security of IT systems.
IT leaders should consider implementing RCA in their organizations as it can be a valuable tool for identifying and resolving problems and improving the overall performance and security of IT systems. By identifying the root cause of a problem, IT teams can take effective corrective action to prevent the problem from recurring, which can improve the overall reliability and stability of IT systems. Additionally, RCA can help to reduce the risk of data loss or security breaches, which is critical for any organization.
However, it's important to note that RCA can be resource-intensive and time-consuming and may not be suitable for all types of problems or incidents. IT leaders should assess the potential benefits of RCA for their organization, and weigh it against the resources that would be required to implement it.
If an organization chooses to implement RCA, it's important to ensure that the appropriate personnel are trained to conduct the analysis and that the appropriate methodologies are used. Additionally, IT leaders should ensure that the results of the RCA are properly documented and communicated to the relevant stakeholders and that the corrective actions are tracked and evaluated for effectiveness.
In summary, IT leaders should consider implementing RCA to identify and resolve problems, improve the overall performance and security of IT systems, and reduce the risk of data loss or security breaches. However, it's important to carefully evaluate the potential benefits of RCA against the resources required to implement it.
Tools for implementing RCA
There are a variety of tools available for implementing Root Cause Analysis (RCA), including:
- Flowcharting tools: Flowcharting tools, such as Visio or Lucidchart, can be used to create visual diagrams of processes and systems. These diagrams can be used to identify the specific steps that led to a problem or incident.
- Mind mapping tools: Mind mapping tools, such as XMind or MindNode, can be used to create visual diagrams of the relationships between different factors and causes. These diagrams can be used to identify the root cause of a problem or incident.
- Statistical analysis tools: Statistical analysis tools, such as Minitab or R, can be used to analyze data and identify patterns or trends that may indicate the root cause of a problem or incident.
- Project management tools: Project management tools, such as Asana or Trello, can be used to track and manage the tasks and actions associated with an RCA.
- Incident management tools: Incident management tools, such as PagerDuty or ServiceNow, can be used to report, track, and manage incidents and problems, and can be integrated with RCA tools to improve the incident resolution process.
- IT Service Management tools: IT Service Management tools, such as ITIL or COBIT, can provide a framework for incident management, problem management, and root cause analysis, and can integrate with other IT service management tools.
It's important to note that the choice of tool will depend on the problem or incident being investigated, the resources available, and the specific needs of the organization. Some organizations may find that a combination of tools is necessary to effectively conduct an RCA.
Information Technology Operations

IT operations refer to the activities involved in maintaining and managing the technology infrastructure and systems of an organization. This includes tasks such as monitoring and maintaining servers, networks, and data centers, as well as troubleshooting and resolving issues as they arise.
In multinational organizations with distributed data centers, server farms, and complex networks, IT operations can be challenging due to the need to manage and coordinate multiple locations and systems. Some of the key methods used to manage IT operations in these organizations include:
- Automation: Automation tools such as scripts and software can be used to automate repetitive tasks and reduce the need for manual intervention. This can improve efficiency and reduce the chances of human error.
- Monitoring: Organizations use various monitoring tools to keep track of the performance and status of their systems and networks. This can help to detect and troubleshoot problems before they become critical.
- Incident management: Incidents such as system failures or security breaches must be handled quickly and efficiently. Having a well-defined incident management process in place can help to minimize the impact of incidents on the organization.
- Disaster recovery: Disasters such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks can have a significant impact on an organization. Having a disaster recovery plan in place can help minimize the impact of a disaster and ensure that the organization can recover quickly.
Best practices for IT operations include:
- Regularly reviewing and updating IT operations processes and procedures
- Keeping software and systems updated to ensure security and performance
- Providing regular training and education for IT staff
- Conducting regular testing of disaster recovery plans and incident management procedures
- Regularly monitoring and analyzing system and network performance to identify potential issues before they occur.
By implementing these best practices and methods, organizations can effectively manage and maintain their IT infrastructure, ensuring that their systems and networks are reliable, secure, and perform at optimal levels.
Automation: Automation tools such as scripts and software can be used to automate repetitive tasks and reduce the need for manual intervention. This can improve efficiency and reduce the chances of human error. Examples of automation tools include configuration management tools like Ansible, Chef, and Puppet, and monitoring tools like Nagios and Zabbix. Automation can also be used for tasks such as software deployments, backups, and scaling.
Monitoring: Organizations use various monitoring tools to keep track of the performance and status of their systems and networks. This can help to detect and troubleshoot problems before they become critical. Examples of monitoring tools include Nagios, Zabbix, and PRTG Network Monitor. These tools can monitor things like server uptime, disk usage, and network traffic.
Incident management: Incidents such as system failures or security breaches must be handled quickly and efficiently. Having a well-defined incident management process in place can help to minimize the impact of incidents on the organization. This process usually includes identifying the incident, assessing the impact, resolving the incident, and documenting the incident for future reference.
Disaster recovery: Disasters such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks can have a significant impact on an organization. Having a disaster recovery plan in place can help minimize the impact of a disaster and ensure that the organization can recover quickly. This plan should include procedures for backing up data, testing recovery procedures, and restoring data and systems.
In summary, automation, monitoring, incident management, and disaster recovery are all critical components of IT operations, and the tools and techniques used in each of these areas play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability, security, and performance of an organization's IT infrastructure.
According to research studies and surveys that have been conducted.
- According to a survey conducted by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), automation is the most widely used tool for IT operations, with 78% of respondents reporting that they use automation to manage their IT operations.
- In a survey by Gartner, it's reported that by 2023, 60% of large enterprises will have adopted artificial intelligence for IT operations (AIOps) to improve incident management and disaster recovery.
- According to a survey by the Enterprise Management Association (EMA), monitoring is the second most widely used tool for IT operations, with 70% of respondents reporting that they use monitoring to manage their IT operations.
- According to a study by Forrester Research, organizations that have a well-defined incident management process in place can resolve incidents up to 70% faster than those that do not.
- According to a survey by the Disaster Recovery Journal (DRJ), nearly 60% of organizations reported that they have a disaster recovery plan in place, but only 25% of those organizations test their plan regularly.
It's worth noting that these statistics are from previous research studies and surveys, and the current situation in the field might have changed. Also, the statistics may vary depending on the specific industry, location, and size of the organization.
Effects Of Positive Thinking and Attitude, on Personal, Spiritual, And Professional Growth

Positive thinking is a powerful tool that can have a profound impact on an individual's personal, spiritual, and career growth in the corporate world. This powerful tool can help individuals overcome obstacles, achieve their goals, and lead a more fulfilling and successful life.
One of the most significant ways in which positive thinking can affect personal growth is by helping individuals develop a more optimistic outlook on life. When people think positively, they are more likely to see the good in situations and focus on the possibilities rather than the limitations. This can help them to overcome challenges and to achieve their goals, which can lead to a greater sense of self-esteem and self-confidence.
Positive thinking can also have a profound impact on spiritual growth. When individuals think positively, they are more likely to see the world in a more positive light and to feel more connected to others. This can help them to develop a deeper sense of meaning and purpose in their lives, which can lead to a greater sense of inner peace and contentment.
In the corporate world, positive thinking can have a significant impact on career growth. When employees think positively, they are more likely to be productive, motivated, and engaged in their work. This can lead to better performance, increased job satisfaction, and greater career advancement opportunities. Additionally, positive thinking can help employees to better handle stress and build stronger relationships with their colleagues, which can lead to a more supportive and productive work environment.
Positive thinking also helps to build up a positive reputation, when a person is known to have a positive attitude, it makes them more approachable and likable. This can help them to build stronger relationships with their colleagues, which can lead to greater career advancement opportunities.
In conclusion, positive thinking is a powerful tool that can have a profound impact on an individual's personal, spiritual, and career growth in the corporate world. By developing a more optimistic outlook on life, individuals can overcome challenges, achieve their goals, and lead a more fulfilling and successful life. Additionally, positive thinking can help to build stronger relationships, increase job satisfaction, and lead to greater career advancement opportunities in the corporate world.
Positive thinking is a powerful tool that can be used to improve one's personal, spiritual, and career growth in the world. It is a mindset that involves focusing on the positive aspects of life and seeing the potential for success in every situation. By adopting a positive attitude, individuals can overcome challenges and achieve their goals in a variety of areas of life.
Personal growth is the process of developing and improving oneself. Positive thinking can help individuals to achieve personal growth by helping them to set and achieve goals. When an individual has a positive attitude, they are more likely to see the potential for success in their endeavors. This can help them to set realistic goals and work towards achieving them. Additionally, positive thinking can help individuals to overcome challenges and setbacks. When faced with a difficult situation, a positive attitude can help individuals to see the situation as an opportunity for growth and learning, rather than as a setback.
Spiritual growth is the process of developing a deeper understanding of one's self, the world, and the spiritual realm. Positive thinking can help individuals achieve spiritual growth by helping them to see the positive aspects of life. When an individual has a positive attitude, they are more likely to see the beauty and wonder in the world around them. This can help them to develop a deeper understanding of the world and their place in it. Additionally, positive thinking can help individuals to overcome negative thoughts and emotions. When faced with negative thoughts or emotions, a positive attitude can help individuals to see the situation in a more positive light, which can help them to find peace and inner balance.
Career growth is the process of developing and advancing in one's career. Positive thinking can help individuals to achieve career growth by helping them to see the potential for success in their careers. When an individual has a positive attitude, they are more likely to see the potential for success in their current job or a new job. This can help them to set realistic career goals and work towards achieving them. Additionally, positive thinking can help individuals to overcome challenges and setbacks in their careers. When faced with a difficult situation, a positive attitude can help individuals to see the situation as an opportunity for growth and learning, rather than as a setback.
In conclusion, positive thinking is a powerful tool that can be used to improve one's personal, spiritual, and career growth in the world. By adopting a positive attitude, individuals can overcome challenges and achieve their goals in a variety of areas of life. Personal growth, spiritual growth, and career growth are all interconnected, and positive thinking can help individuals achieve all of these goals. It is important for individuals to recognize the power of positive thinking and to make it a part of their daily lives. By doing so, they can achieve success and fulfillment in all areas of their lives.
Positive thinking and attitude are powerful tools that individuals can use to affect personal, spiritual, and career growth in the world. These tools can help individuals overcome obstacles, achieve their goals, and create a more meaningful and fulfilling life.
Positive thinking is the practice of focusing on the good in any situation, rather than the negative. It is the ability to see the potential for success, even when faced with challenges. Positive thinking can help individuals develop a more optimistic outlook on life, which can lead to better mental and physical health, as well as increased resilience and perseverance.
A positive attitude, on the other hand, is how an individual perceives and responds to the world around them. A positive attitude can be characterized by a sense of gratitude, appreciation, and optimism. It is the ability to see the good in people and situations and to respond with kindness and understanding. A positive attitude can help individuals to build stronger relationships, to be more productive, and to achieve greater success in their personal and professional lives.
Together, positive thinking and attitude can be used to achieve personal, spiritual, and career growth in the world. For example, an individual with a positive attitude and mindset can use these tools to overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. They can set clear and realistic goals, and use positive affirmations and visualization techniques to stay motivated and focused. They can also use positive thinking and attitude to develop a stronger sense of self-worth, which can help them build stronger relationships and achieve greater success in their personal and professional lives.
In terms of personal growth, positive thinking and attitude can help individuals to overcome negative self-talk and to develop a more positive self-image. They can also help individuals develop better problem-solving skills, which can lead to greater resilience and perseverance. A positive attitude can help individuals to be more grateful and appreciative, which can lead to greater happiness and fulfillment.
In terms of spiritual growth, positive thinking and attitude can help individuals develop a deeper sense of purpose and meaning in their lives. They can help individuals to connect with their inner selves, and to develop a deeper understanding of their spiritual beliefs and values. A positive attitude can also help individuals to be more compassionate and empathetic, which can lead to greater inner peace and contentment.
In terms of career growth, positive thinking and attitude can help individuals to achieve greater success in their professional lives. They can help individuals to develop better communication skills, build stronger relationships with their colleagues and clients, and be more productive and efficient. A positive attitude can also help individuals to be more optimistic and resilient, which can lead to greater success in the face of challenges and setbacks.
In conclusion, positive thinking and attitude are powerful tools that individuals can use to affect personal, spiritual, and career growth in the world. By developing a positive attitude and mindset, individuals can overcome obstacles, achieve their goals, and create a more meaningful and fulfilling life. They can also use these tools to develop a deeper sense of purpose, build stronger relationships, and achieve greater success in their personal and professional lives. Therefore, individuals must adopt positive thinking and attitude as a lifestyle and practice it every day to achieve their full potential and bring positive change in the world.
Here are a few ways to cultivate positive thinking and a positive attitude:
1. Practice gratitude by regularly expressing appreciation for the good things in your life.
2. Reframe negative thoughts into positive ones. For example, instead of thinking "I can't do this," try thinking "I can do this, and I will find a way."
3. Surround yourself with positive people who uplift and support you.
4. Engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
5. Practice mindfulness and meditation to help you stay present and focused.
6. Set realistic and achievable goals for yourself and work towards them consistently.
7. Find humor in difficult situations.
8. Practice self-compassion by treating yourself with kindness and understanding.
9. Cultivate an attitude of optimism by looking for the good in every situation.
10. Help others and make a positive impact in their lives.
Remember that cultivating positive thinking and a positive attitude takes time and practice, but with dedication, it can lead to a more fulfilling life.
Here are a few ways to use positive thinking and a positive attitude for healing
- Start each day with a positive mindset: Wake up each morning with a positive attitude and set intentions for the day ahead. This can include things like being grateful for what you have, focusing on the present moment, and being open to new opportunities.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness is the practice of being present at the moment and focusing on your thoughts and feelings without judgment. This can help reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
- Surround yourself with positive people: The people you surround yourself with can greatly influence your thoughts and attitudes. Surround yourself with people who inspire and uplift you, and avoid those who bring negativity into your life.
- Speak positively to yourself: The way you talk to yourself can have a big impact on your mental and emotional well-being. Practice speaking positively to yourself, and avoid negative self-talk.
- Focus on the good: When things go wrong, it can be easy to focus on the negative. Instead, try to focus on the good in any situation and look for the silver lining.
- Take care of your physical health: Taking care of your physical health is important for overall well-being. This includes getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep.
- Practice gratitude: Practice being grateful for what you have in your life. This can help shift your focus from what you lack to what you have and can improve your overall mood and well-being.
- Practice forgiveness: Holding onto resentment and anger can harm your mental and emotional well-being. Practice forgiveness, and let go of negative emotions that may be holding you back from healing.
How to propagate spiritual well-being
- Start by setting a positive intention for your day. This can be as simple as saying to yourself, "I choose to have a positive attitude today."
- Practice gratitude by focusing on the things in your life that you are thankful for. This can be done by writing a gratitude journal or simply reflecting on your blessings throughout the day.
- Use positive affirmations to change your thoughts and attitudes. Repeat positive phrases to yourself such as "I am strong" or "I am capable" to boost your self-esteem and confidence.
- Practice mindfulness by being present at the moment and focusing on your breath. This can help you to release negative thoughts and emotions and increase feelings of peace and calm.
- Surround yourself with positive people and engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment. This can include spending time with loved ones, participating in hobbies, or volunteering in your community.
- Finally, make sure to take care of your physical and emotional well-being by getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise. This will help to support your overall spiritual well-being.
The Connected Car
A connected car is a vehicle that is connected to the internet and can share data with other cars, as well as with the infrastructure around it. This allows the car to access real-time information and make decisions based on that data. The technologies used in connected cars include:
1. Cellular connectivity: This allows the car to connect to the internet and share data with other cars and the infrastructure around it. This can be done through cellular networks such as 4G or 5G.
2. GPS: This allows the car to determine its location and navigate to a destination.
3. Sensors: These include cameras, lidar, radar, and other sensors that gather data about the car's environment, such as the location of other vehicles and obstacles.
4. Cloud computing: This allows the car to share data with the cloud and process that data, which can be used to make decisions and provide real-time information to the driver.
The future of connected cars is expected to involve the continued development and integration of these technologies, as well as the adoption of new technologies such as 5G connectivity and edge computing. This will allow cars to access even more data and make better decisions in real time. Additionally, it is expected that cars will be able to communicate with each other and with the infrastructure around them to increase safety and efficiency on the road.
About AI, connected cars will be able to use the data they gather to make decisions and provide real-time information to the driver. This will include recognizing and identifying objects in the environment, predicting the behavior of other vehicles and pedestrians, and planning the most efficient and safe route to a destination. Additionally, the cars will be able to communicate with each other and with the infrastructure around them to coordinate their movements and increase safety and efficiency on the road.
In conclusion, connected cars are vehicles that are connected to the internet and can share data with other cars, as well as with the infrastructure around them. They use technologies such as cellular connectivity, GPS, sensors, and cloud computing to access and process data. The future of connected cars is expected to involve the continued development and integration of these technologies, as well as the adoption of new technologies such as 5G connectivity and edge computing. Additionally, AI will play a big role in decision-making, providing real-time information to the driver and coordinating movements with other cars and the infrastructure around them.
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, are vehicles that are capable of sensing their environment and navigating without human input. They use a combination of technologies such as sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand their surroundings and make decisions about how to move.
One key technology used in self-driving cars is lidar, which uses lasers to create a 3D map of the vehicle's environment. This allows the vehicle to detect and avoid obstacles, as well as to understand its location and orientation. Other sensors, such as cameras and radar, are also used to gather information about the environment and to provide additional data to the vehicle's AI system.
Another important technology used in self-driving cars is AI, which allows the vehicle to make decisions and navigate based on the data it receives from its sensors. This includes recognizing and identifying objects in the environment, predicting the behavior of other vehicles and pedestrians, and planning the most efficient and safe route to a destination.
The future of self-driving cars is expected to involve the continued development and integration of these technologies, as well as the adoption of new technologies such as 5G connectivity and edge computing. This will allow self-driving cars to be even more accurate, reliable, and safe.
About connected cars, self-driving cars will take connectivity to a whole new level. Connected cars are vehicles that are connected to the internet and can share data with other cars, as well as with the infrastructure around them. Self-driving cars will be able to take advantage of this connectivity to share data with other cars on the road, as well as with traffic lights, stop signs, and other infrastructure. This will allow them to make more informed decisions, such as adjusting their speed to avoid congestion or taking an alternative route to avoid an accident. The cars will also be able to communicate with each other to coordinate their movements, which will help to increase safety and efficiency on the road.
Self-driving cars use a combination of technologies such as sensors, cameras, radar, and AI to understand their environment and navigate without human input. The future of self-driving cars is expected to involve the continued development and integration of these technologies, as well as the adoption of new technologies such as 5G connectivity and edge computing. They will also take advantage of the connectivity features of connected cars to share data with other cars and infrastructure, which will increase safety and efficiency on the road.
DevOps a Practitioner's Approach
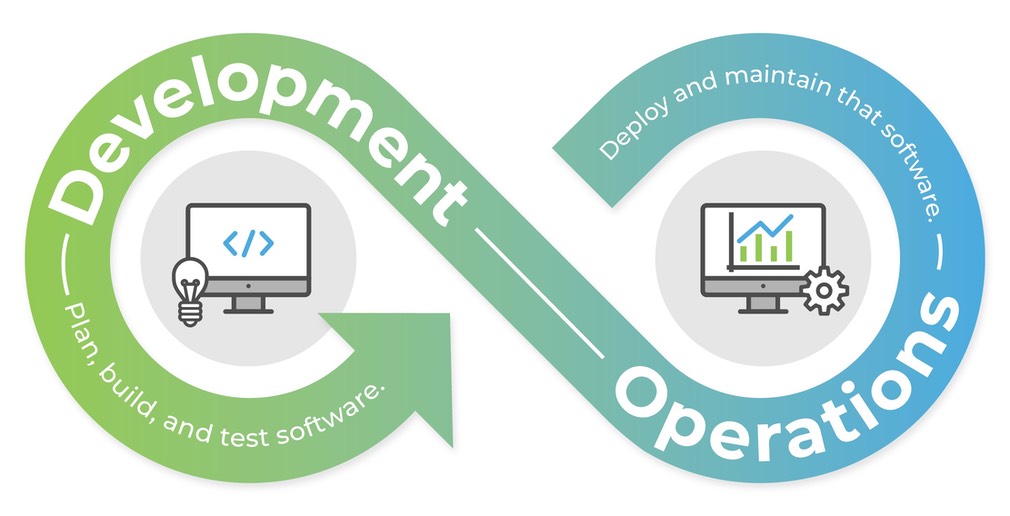
DevOps is a methodology that emphasizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams to improve software releases' speed and quality. As a practitioner, it is important to understand the principles of DevOps and how to apply them in a real-world setting.
The first step in implementing DevOps is to automate as many tasks as possible. This can be done using tools such as Jenkins, Travis CI, and Ansible. Automation allows teams to increase efficiency and reduce the risk of errors. It also allows teams to focus on more important tasks, such as creating new features and fixing bugs.
Next, it is important to implement a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. This allows teams to constantly integrate code changes and deliver them to customers as soon as they are ready. This helps to reduce the time between code changes and deployment, which can be critical in today’s fast-paced business environment. Tools such as Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab can be used to implement a CI/CD pipeline.
The principles of DevOps include:
- Automation: using tools and scripts to automate repetitive tasks and increase efficiency
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD): constantly integrating code changes and delivering them to customers as soon as they are ready
- Monitoring and logging: monitoring the performance and behavior of systems in production to quickly detect and diagnose issues
- Cultural shift: fostering a culture of collaboration and communication across teams, breaking down silos, and promoting a shared responsibility for the success of software releases.
The advantages of DevOps include:
- Faster and more reliable software releases: by automating tasks and constantly integrating and delivering code changes, DevOps allows teams to release software faster and with fewer errors
- Improved collaboration and communication: DevOps promotes a culture of collaboration and communication across teams, leading to a more efficient and effective software development process
- Greater visibility and control: through monitoring and logging, teams can gain greater visibility into the performance and behavior of systems in production, allowing them to quickly detect and diagnose issues
- Increased agility: DevOps allows teams to respond quickly to changing business requirements and customer needs.
The disadvantages of DevOps include:
- High initial investment: implementing DevOps requires a significant investment in tools, automation, and processes, which can be costly for organizations
- Cultural change: adopting DevOps requires a cultural change within organizations, which can be difficult and time-consuming
- Requires skilled workforce: DevOps requires a skilled workforce with a deep understanding of both development and operations, which can be difficult to find and retain
- Complexity: DevOps can introduce a lot of complexity in the software development process, which can make it harder to troubleshoot and fix issues.
The scope of DevOps includes:
- Software development: DevOps is primarily focused on improving the software development process, from code creation to deployment and maintenance
- Operations: DevOps also includes operations and infrastructure, such as monitoring, logging, and incident response
- Collaboration: DevOps promotes collaboration and communication across teams, breaking down silos and promoting a shared responsibility for the success of software releases.
DevOps is not just a set of tools, but an approach that can be applied to any software development process and organization. It can be applied to any organization that wants to improve the speed and quality of software releases.
Monitoring and logging are also critical to the success of DevOps. This allows teams to gain visibility into the performance and behavior of systems in production. By monitoring and logging, teams can quickly detect and diagnose issues, which helps to reduce downtime and improve the overall performance of systems. Tools such as Prometheus, Elasticsearch, and Grafana can be used for monitoring and logging.
In addition to the technical aspects of DevOps, it is also important to foster a culture of collaboration and communication across teams. This helps to break down silos and promote a shared responsibility for the success of software releases. This can be done by encouraging cross-functional teams and promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
Finally, it is important to remember that DevOps is not a one-time event but a continuous process. As a practitioner, it is important to constantly evaluate and improve the organization's process, tools, and culture. This will help to ensure that the organization is always at the forefront of the latest best practices and technologies.
In conclusion, DevOps is a methodology that emphasizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams to improve the speed and quality of software releases. By automating tasks, implementing a CI/CD pipeline, monitoring and logging, fostering a culture of collaboration and communication, and continuously improving the process, practitioners can successfully implement DevOps in their organizations.
The future of DevOps is likely to continue evolving and expanding, with a focus on increased automation, enhanced security, and greater emphasis on collaboration and communication across teams. Some specific trends that are expected to shape the future of DevOps include:
1. Increased Automation: With the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning, automation is expected to become even more prevalent in the DevOps process. This will help to further increase the speed and reliability of software releases.
2. Enhanced Security: As cyber threats continue to evolve, the focus on security in the DevOps process will become increasingly important. This will involve integrating security into the entire software development lifecycle, from development to deployment and maintenance.
3. Greater Emphasis on Collaboration and Communication: With the increasing adoption of remote work, the emphasis on collaboration and communication across teams will become even more important. This will involve the use of more advanced collaboration tools and the integration of more real-time communication channels.
4. Cloud-Native and Microservices: The shift towards cloud-native and microservices architecture will continue to gain momentum. This will involve breaking down monolithic applications into smaller, more manageable components that can be deployed and scaled independently.
5. Continuous experimentation: With the increasing adoption of A/B testing, experimentation will become a critical part of the DevOps process. This will allow teams to validate and optimize the software development process by experimenting with different approaches.
6. DevSecOps: The integration of security practices in the DevOps process is becoming more and more important, therefore DevSecOps approach will become more common.
Overall, the future of DevOps is likely to involve increased automation, enhanced security, and greater emphasis on collaboration and communication across teams, all aimed at improving the speed and reliability of software releases.
The Connected World

The Connected World: How the Internet of Things is Changing Our Lives
In the past few decades, the internet has transformed the way we live and work. It has connected us to an endless wealth of information, people, and resources, and has made it easier for us to communicate, collaborate, and innovate. But the internet is no longer just a tool for humans - it is also a tool for things.
Welcome to the connected world, also known as the Internet of Things (IoT).
The IoT refers to the growing network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects that are connected to the internet and can collect and exchange data. These connected devices can range from smart thermostats and security cameras to industrial machines and agricultural sensors. They are equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity that allow them to communicate with each other and with people, often through the cloud.
The IoT is making our lives more convenient and efficient in several ways. Smart home devices, for example, can help us save energy, reduce our carbon footprint, and improve our quality of life. We can use smart thermostats to remotely control the temperature of our homes, smart appliances to monitor our energy usage, and smart security systems to protect our homes and families.
But the IoT is not just about making our personal lives easier. It is also transforming industries and changing the way we work. For example, the IoT is helping to improve the efficiency of supply chains, manufacturing, and agriculture. It is enabling companies to track and optimize their assets, reduce waste and downtime, and improve the quality of their products and services.
The IoT also drives new business models and creates new opportunities for entrepreneurs and innovators. It is enabling companies to offer subscription-based services, monetize data, and create new revenue streams. It is also creating new opportunities for people to work remotely, collaborate more effectively, and create value for customers.
However, the IoT is not without its challenges. There are concerns about privacy, security, and the potential impact on jobs and society. There are also technical challenges, such as interoperability, scalability, and the need for robust infrastructure and standards.
These challenges will need to be addressed as the IoT grows and evolves. But there is no denying that the connected world is here to stay and will continue to shape how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
What is Metaverse
The term "metaverse" was coined by science fiction author Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash and refers to a virtual shared space where users can interact with each other and with virtual objects and environments. It is essentially an immersive, virtual world that can be accessed through the internet.
The metaverse has many potential applications, ranging from entertainment and gaming to education and business. In the entertainment industry, the metaverse could be used to create virtual reality experiences, allowing users to fully immerse themselves in a fictional world. This could include everything from virtual theme parks to interactive movies. The gaming industry is also exploring the potential of the metaverse, with companies working on creating virtual worlds where players can interact with each other in real-time.
The educational potential of the metaverse is vast, as it could allow for the creation of virtual classrooms and training simulations. For example, students could participate in virtual field trips or lab experiments, or professionals could receive virtual training for their jobs. The metaverse could also be used for remote collaboration, allowing people to work together in a virtual environment as if they were in the same physical location.
The metaverse could be used in the business world for everything from virtual meetings and conferences to virtual trade shows and product demonstrations. It could also be used for virtual real estate, allowing people to buy and sell virtual property in a virtual world.
The development of the metaverse is still in its early stages, and several technical and logistical challenges need to be overcome. For example, creating a seamless, immersive virtual world that can be accessed by a large number of users at once requires significant technological advancements. There are also ownership and control issues in the metaverse, as it is unclear who would have jurisdiction over virtual property and interactions.
Despite these challenges, the potential of the metaverse is vast, and we will likely see significant developments in this area in the coming years. As technology continues to advance and more people become interested in virtual reality experiences, the metaverse could become an integral part of our daily lives. It could change the way we work, play, and interact with each other, opening up a whole new world of possibilities.
WEB3 Explained

Web3, also known as the decentralized web, is a term that refers to the use of blockchain technology and decentralized protocols to create a more secure and transparent internet. It has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact and conduct business online, offering numerous advantages over the current centralized web (web2).
One of the main advantages of web3 is its ability to provide greater security and privacy for users. In the current centralized web, large tech companies and government agencies have access to vast amounts of personal data, which can be vulnerable to hacking and misuse. With web3, data is stored on decentralized networks and can only be accessed with the permission of the user, making it much harder for outsiders to access sensitive information.
Another advantage of web3 is its potential to create more transparency and accountability in online interactions. In a decentralized system, there is no central authority controlling the flow of information, making it difficult for individuals or organizations to manipulate data for their gain. This can lead to greater trust and confidence in online transactions and interactions.
Web3 technologies are made up of several different components, including blockchain, peer-to-peer networks, and smart contracts. Blockchain technology is the foundation of web3, providing a decentralized, secure way to store and transfer data. Peer-to-peer networks allow users to directly connect, rather than relying on central servers, which can be vulnerable to attacks. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. They allow for the automation of many online interactions, making them faster, cheaper, and more efficient.
The future of web3 looks bright, with many experts predicting that it will become an integral part of our daily lives. Already, there are numerous decentralized applications (dApps) being developed that utilize web3 technology, ranging from social media platforms to supply chain management systems. As more and more people become aware of the benefits of web3, we will likely see widespread adoption of decentralized technologies in the coming years.
In conclusion, web3 has the potential to greatly improve the security, privacy, and transparency of the internet. Its use of blockchain, peer-to-peer networks, and smart contracts makes it a powerful tool for creating a more decentralized and trustworthy online environment. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see web3 becoming an increasingly important part of our daily lives.
Corporate Cyber Security: Trends and Challenges

As the world becomes more connected, the need for corporate cyber security is greater than ever. Cyber-attacks and data breaches can have serious consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. To protect against these threats, companies must stay up-to-date on the latest trends and challenges in corporate cyber security.
Here are some key trends and challenges in corporate cyber security:
- Increased adoption of cloud and remote work: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift to cloud and remote work, which brings new security challenges. Companies must ensure that their data is secure in the cloud and that their remote employees have access to the tools and resources they need to stay productive and secure.
- The growing sophistication of cyber-attacks: Cyber criminals are becoming more sophisticated and using increasingly sophisticated techniques to gain access to corporate systems. Companies must stay vigilant and invest in robust security measures to protect against advanced threats.
- The increasing importance of data privacy: With new data protection laws and regulations, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), companies must ensure that they are complying with data privacy requirements and protecting their customers' data.
- Need for better security awareness and training: Cybersecurity is not just a technical issue - it is also a human issue. Companies must educate their employees on the importance of cyber security and provide them with the training and resources they need to stay safe online.
- Increasing reliance on third-party partners: Many companies rely on third-party partners, such as suppliers, vendors, and contractors, to conduct business. These partners can create new security risks, and companies must ensure that they are adequately protected.
To address these trends and challenges, companies must adopt a comprehensive and holistic approach to cyber security. This includes investing in the right technologies, such as firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems, as well as in the right people, processes, and policies.
Companies must also be prepared for the unexpected and have a plan in place to respond to cyber-attacks and data breaches.
In conclusion, corporate cyber security is an increasingly important issue that requires ongoing attention and investment. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends and challenges and adopting a holistic approach to cyber security, companies can protect their systems, data, and reputation and thrive in the connected world.
